Black Widow Spider Safety and PPE
Posted by Anthony Webb on Nov 25th 2024
You would likely be hard-pressed to find someone who has never heard of a black widow spider. They are well-known for their striking appearance and are the most venomous spider found in North America.
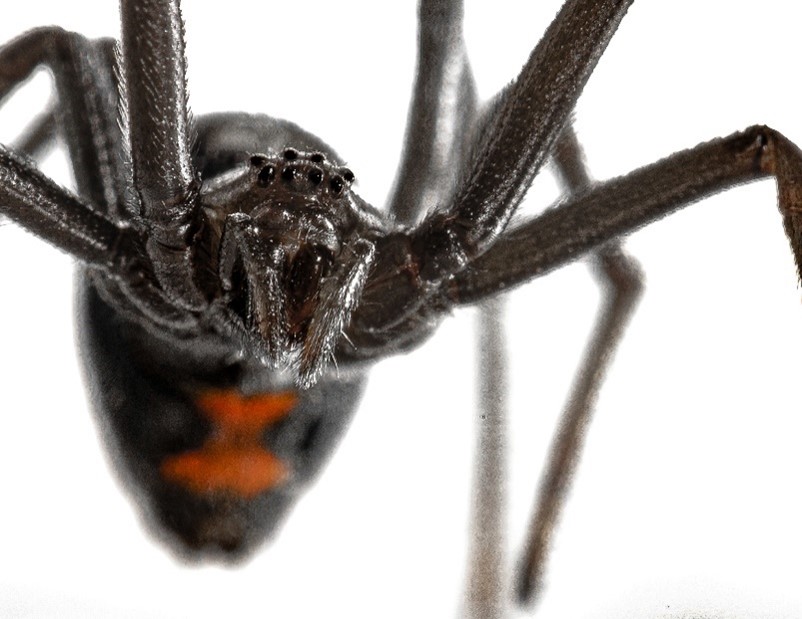

The females’ distinctive red marks make black widows one of the most recognized spiders.
Female black widows are hazardous and have the potential to inject a toxic venom that is roughly 15 times more lethal than a rattlesnake’s venom. Thankfully, these spiders are smaller than snakes, which means they carry less venom.
As seasonal temperatures increase in April and May, outdoor jobs begin ramping up. And once temperatures reach 70 degrees, black widows become more active, and their mating season kicks off. Staying protected is essential if one has any concerns these dangerous creators are nearby. This article highlights what you should know to protect yourself around black widow spiders—from their natural habitats to some common questions involving how to stay safe at work if your job puts you close to this eight-legged hazard.
Identification
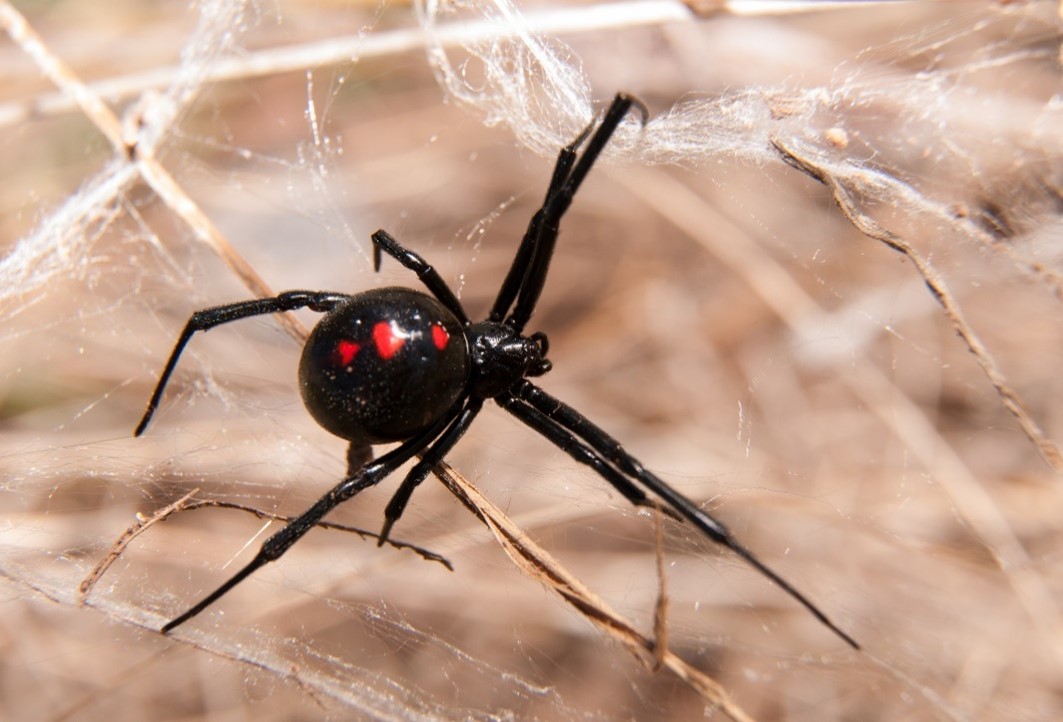

The southern black widow spider is easily identified by its characteristic shiny black body and striking red or orange hourglass-shaped marking on the underside of the abdomen.
The northern black widow features spots down its upper surface and two crosswise bars. Its shape is more round, measuring roughly 1.5 inches in length. Male black widow spiders are roughly one-half the size of females.
Habitat

Where do black widow spiders live? They prefer dry, rarely disturbed, dimly lit, or dark locations. In North America, black widow spiders are located mainly in the south and west; however, species have been found across all 50 states.
Black widows are known to construct their webs in dark corners of homes or sheltered areas of buildings. These spiders prefer to set their messy webs in areas that offer more potential shelter for their prey. This makes basements, closets, garages, and sheds ideal homes for black widows. In cooler climates, these spiders will search for locations that will remain warm and dark during cold winter months, such as hot pipes found under a house.
Interesting Facts

Though its name is infamous throughout the world, the black widow’s reputation as the most venomous spider has been exaggerated. The most dangerous spiders in the world are the Australian funnel-web spider and the Brazilian wandering spider. However, the black widow is the most venomous spider in North America. Here are some exciting details about black widows to help differentiate between fact and fiction.
- The scientific name for a black widow is Latrodectus. There are 31 species of widow spiders in the Latrodectus genus. In North America, each region has its unique species. The western species is Latrodectus Hesperus; the northern species is Latrodectus Variolus, and the southern species is Latrodectus mactans.
- Black widows expose their bright red marking as a warning to predators. Researchers have observed that spiders without bright red coloring are attacked by predators three times more often than those with a red hourglass.
- Black widow toxin contains a chemical called alpha-latrotoxin that rapidly engulfs nerve cells.
- Since these spiders like darkness, they are most active during nighttime.
- Only the larger female can inflict a hazardous bite; the rarely seen smaller male is often harmless.
Bite Concerns
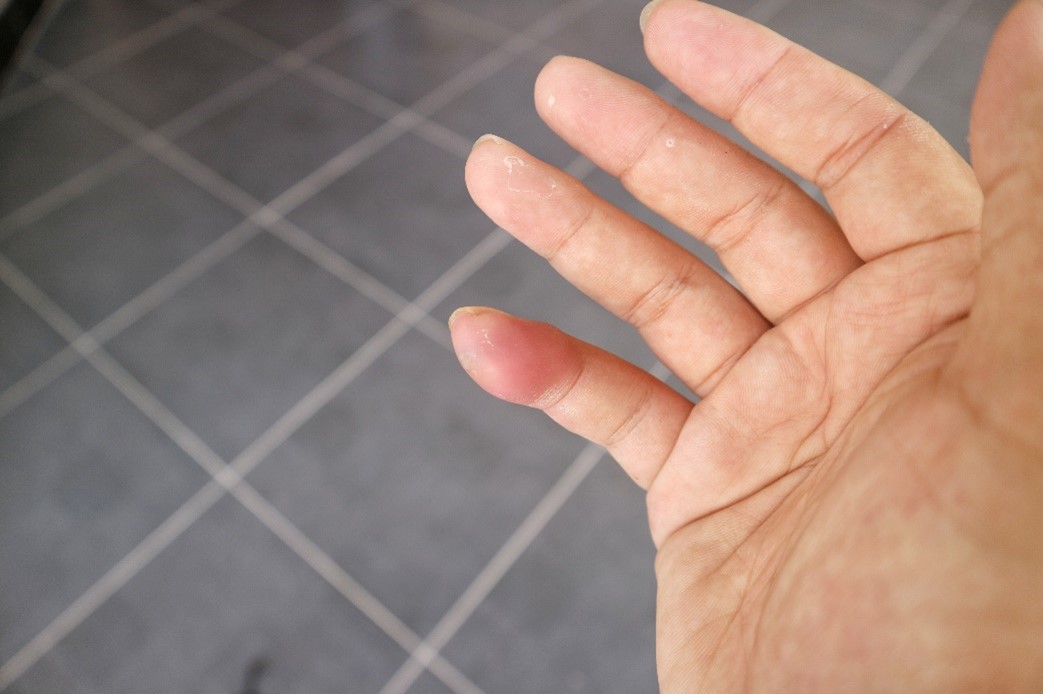
A black widow bite will often have a sensation like a pinprick and is identifiable by the two puncture marks left on the skin. However, don’t let that quick poke feeling fool you. Black widow venom affects the human nervous system and can have deadly consequences for those with severe reactions, though the severity varies from person to person. Directly after being bitten, you may feel pain at the site of the bite, followed by redness or swelling. More intense reactions can include nausea, muscle aches, or difficulty breathing.
WebMD highlights all the typical symptoms of a black widow bite. Here are the most common:
- Muscle aches and stiffening
- Vomiting
- Trouble breathing
- Severe abdominal discomfort and cramping
- Extreme sweating
- Rash
- Inflamed eyelids
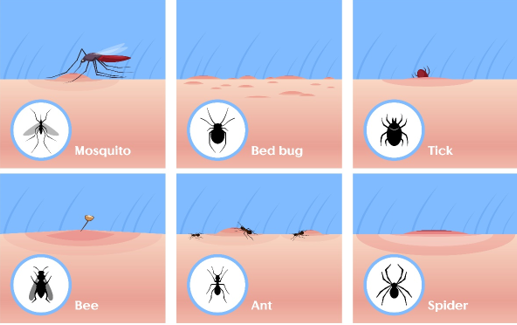
A Visual Aid for Different Types of Insect Bites
If you have any reason to believe you’ve been bitten by a black widow spider, immediately call 911. It’s also important to remember that black widow bites can be fatal in young children and the elderly due to the type of venom found in black widows. You’ll want to take these victims to the emergency room right away.
The good news is that these spiders generally only bite if disturbed or surprised. Bites are likely to occur when people directly contact their webs. Our next section highlights the most common work-related places where these critters are found.
Work Hazards

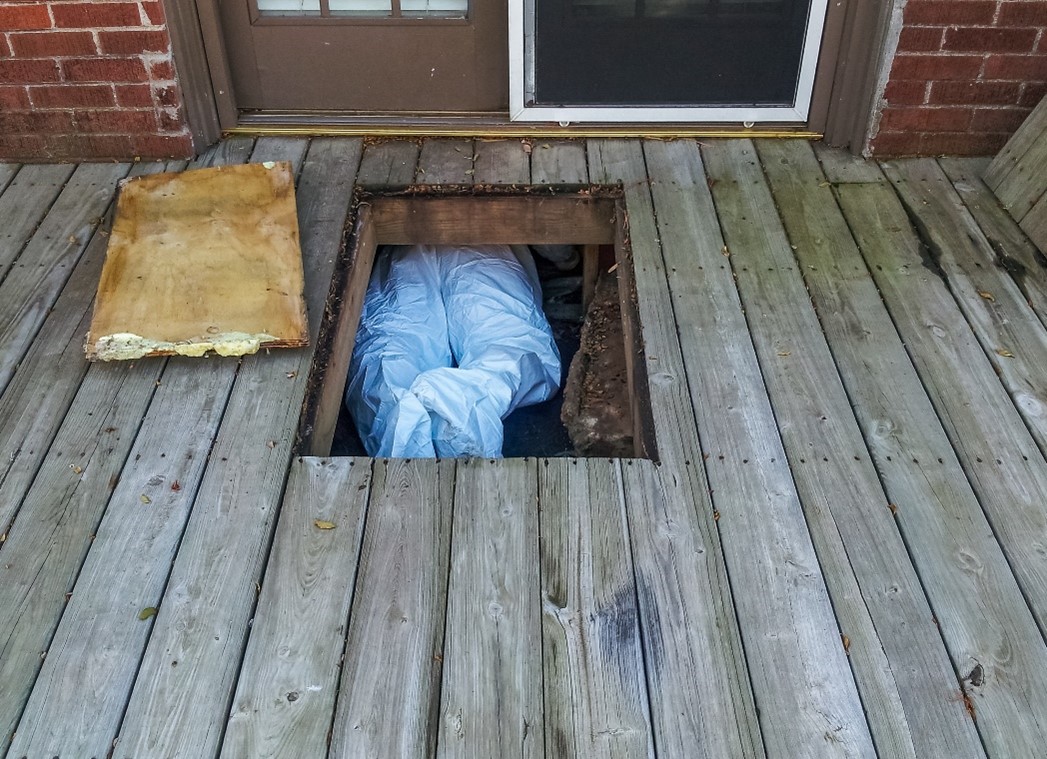
For the most part, black widows quietly coexist near people with little contact or danger. However, when individuals begin operating in areas where these spiders make their home, there is cause for concern. What’s most troubling is that few people consider black widows a potential hazard that workers may encounter. There are several common areas where black widows like to hang out that workers often visit.
Here is a list of areas where these spiders like to live and the workers who may be affected when they operate in these places:
- Crawl spaces under homes and attics where HVAC workers run pipe and install ductwork.
- Under bricks, rocks, and stones that gardeners often lift
- Under boards moved and utilized by construction workers.
- Inside boxes and furniture moved by moving companies.
- Near debris and rubble piles that are located at worksites, especially construction sites
- Drainage pipes serviced by plumbers
- Sheds and barns used in agricultural activities, such as on a farm.
- Well houses and root cellars repaired by tradespeople.
- Buildings and outdoor work sites cleaned by janitors and laborers.
- Small trees and bushes trimmed by landscaping crews.
- Fences and decks mended by construction workers and tradesmen.
- Hollow logs encountered by logging crews.
- Meter boxes read by utility workers.
In addition to the above list, the following areas are also popular homes for black widows: fire piles, woodpiles, and under loose bark.

If it’s a dark area, be on guard.
OSHA and Work Protection

The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides insight into the protection workers should consider wearing if poisonous spiders are a potential hazard. Here are some suggestions for personal protective equipment (PPE) that might be worn when working around potential spider dangers:
- Wear safety clothing that covers the entire body. During the summer months, workers often wear MCR Safety’s hi-vis moisture-wicking shirts, which will help cover and protect a person’s arms. Our rain gear and protective DuPont™ Tyvek® suits also cover workers’ bodies.

- Wearing protective work gloves is one of the easiest ways to safeguard one’s hands from a spider bite, especially those reinforced with extra material. Our article on heavy-duty gloves provides insight into options you should consider.

Fully coated gloves with protection up the arms is an ideal form of protection, like the CP14R.
Another way to protect against spider bite dangers is to always inspect work areas for spiders or spider webs before beginning any work. Always assume there is a possibility that black widow spiders will be present. Be extremely careful when reaching into quiet, dark spaces or cleaning areas where things have been stored undisturbed for lengthy periods. Never put your hands into spider webs, and never underestimate the hiding places where these spiders could appear.
Common Questions

What to do when you find a black widow spider?
- Black widows love to live in dark and cluttered areas like basements and garages, so it might be a good time to clean the house and declutter if you find a black widow or evidence of webs in one of these areas. Try to keep work areas clean and remove clutter from garages and worksites, eliminating potential hiding spots.
What does a male black widow spider look like?
- Female black widows have the classic shiny black body with the bright red triangles, but black male widows are plainer, can be either black or grey, and do not typically have the trademark red hourglass shape. It’s essential to know the difference because if you are dealing with a female, there is always the risk that she has laid eggs somewhere in your house.
Do wolf spiders eat black widows?
- Wolf spiders are opportunistic and hunt what is readily available to them. They often cannibalize other spider species, but because of the potent venom in black widows, wolf spiders prefer other means of nutrition. That being said, yes, a wolf spider may eat a black widow if they need to.
How to get rid of black widow spiders in my yard?
- Encouraging black widows to stay off your property entirely will aid in keeping your home free of these nasty pests. To keep black widows from moving into your yard, start by removing any favorite web-building spots such as woodpiles or high grass. Adding birds to your yard via a bird feeder can also keep black widows at bay.
Protecting Workers in Dark Areas

Black widows can pose a severe threat to anyone who primarily works outdoors or in dark areas. Unfortunately, employers often overlook this danger, so arm yourself with the knowledge you need to keep yourself safe. And consider wearing MCR Safety PPE to shield your body from these venomous pests!
Click the below image to leave us comments, questions, or any concerns.
For over 45 years, MCR Safety has proven to be a world leader in gloves, glasses, and garments. Whether it's lifting rocks, crawling under a house, or working at a construction site, we provide solutions to workplace hazards. It's all part of our commitment to protect people.
No matter your industry, we have the personal protective equipment you need.

Learn more about MCR Safety by checking out our most recent video. For more information, browse our website, request a catalog, find a distributor, or give us a call at 800-955-6887.

