
“Great companies are built on great products.”
In 2017, Elon Musk’s automobile company, Tesla, became one of the world’s most valuable car companies. The electric-car manufacturer’s market value came in at $56.1 billion, with GM close behind at $51.6 billion.
Tesla may be the talk of the town today, but it is just one in a long line of automobile manufacturers. Back in 1885, Carl Benz developed the first automobile. Known as the Benz Patent “Motorwagen”, his creation is considered by many as the birth of the automobile. It certainly changed transportation history forever.

The "Motorwagen" changed the way people moved.
Over one hundred years after Benz developed his Motorwagen, the automobile remains the dominant form of transportation across the United States. With the world's reliance on motor vehicles, there is a strong demand for new car production, along with parts manufacturing to keep older cars on the road through regular repairs and maintenance.
Today's automotive and motor vehicle manufacturing industry is one of the top employment industries in the world. From Tier 1 and Tier 2 parts suppliers to factories and assembly lines to the repair and maintenance of vehicles, the automotive industry is critical to the global economy's health and indirectly supports millions of jobs.
Within each automotive sub-industry, there is great demand for personal protective equipment, or PPE, which is where MCR Safety enters the picture. MCR Safety recognizes how important knowledge and information is in keeping workers safe from workplace hazards, which is why we've assembled a variety of automotive resources in one spot.
Across all of MCR Safety’s Automotive Industry pages, we highlight each specific industry, employment numbers, worker activities performed, potential hazards, and, most importantly, the safety gear necessary to help keep automotive workers safe. You can either jump directly to the areas of automotive that apply to you, or you can stay on this main page for a macro overview of this very important industry.
Here are the six different industries highlighted across MCR Safety's Automotive Industry pages:
| Automotive Industry | NAICS Code |
|---|---|
| Engine manufacturing | 33631 |
| Parts manufacturing | 3363 |
| Repair and maintenance | 8111 |
| Tire Manufacturing | 32621 |
| Trailer manufacturing | 3362 |
| Vehicle Manufacturing | 3361 |
The automotive industry is an excellent barometer and gauge for overall economic activity. This is because it affects multiple industries, from the materials going into vehicles to the aftermarket support in keeping them running. In fact, in a recent PBS Frontline documentary, a Chinese car manufacturer notes that the car industry is representative of an entire country's industry, a bellwether of it's economic performance. The automotive industry involves the assembly of all technologies: cybersecurity, electrical, lighting, mechanical, and software. All industries must be strong before an automobile can be built, meaning a country is highly advanced.
In addition, manufacturing motor vehicles requires immense resources. Large quantities of materials from other industries go into building vehicles. These materials include steel, iron, aluminum, carpeting, textiles, rubber, plastics, and glass. According to the American Chemical Council, plastic encompasses about 50% of the construction of a new car. It is used in places like door handles, dashboards, seat belts, and air conditioner vents.
Most automobiles still rely on petroleum to operate, making vehicles still the lifeblood of the oil and gas industry.
You hear a lot in the news today about how automotive manufacturing is leaving the
U.S. Well, one may want to also pause and reflect on the fact that this is happening as worldwide
production
is at an all-time high. In
2000, there were 58 million vehicles produced. In 2018, there was a total of 95 million vehicles
produced. That is over 38% growth during an eighteen year period.
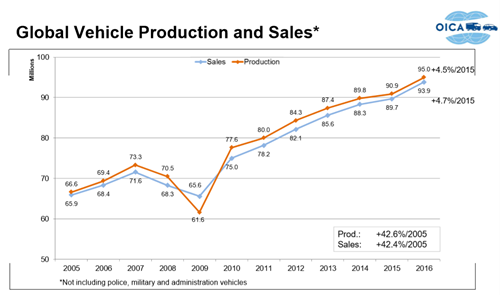
By 2040, cars are projected to reach two billion, with most of the growth taking place in China and India. This projected number means car manufacturing will continue to increase for decades to come. As you can see in the charts below, China's automotive market production is a big reason for the overall growth.
The automotive industry is comprised of some of the world's largest companies. The largest automakers in the U.S., known as "The Big 3", are Ford, GM, and Chrysler. However, many of the world's largest automotive companies have their own production operations in the U.S., which ultimately means they create U.S. jobs.
Here is a look at the top automotive companies employing the most workers.
| Company | Worldwide Employees |
|---|---|
| Volkswagen | 642,000 |
| Nissan | 450,000 |
| Toyota | 369,124 |
| Fiat Chrysler | 235,915 |
| Honda North America, Inc. | 208,000 |
| Ford Motor Company | 199,000 |
| General Motors Company | 173,000 |
| Hyundai | 104,731 |
| Tesla, Inc. | 45,000 |
| Suzuki | 45,000 |

OICA's Worldwide Employment Numbers by Country
The automotive industry creates jobs, jobs, and more jobs. The American Automotive Policy Council highlights that the auto industry supports a total of nearly 8 million American jobs. These jobs are found in a wide range of facilities: laboratories, factory floors, assembly lines, engine plants, metal stamping, and dealerships. When you examine automotive manufacturing, The Big 3 make up more than 66% of U.S. auto industry jobs.

Production positions still make up a large percentage of workers.
| Industry | Employment | NAICS |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive repair and maintenance | 886,600 | 8111 |
| Motor vehicle parts manufacturing | 654,700 | 3363 |
| Motor vehicle manufacturing | 236,500 | 3361 |
| Motor vehicle body and trailer manufacturing | 178,800 | 3362 |
| Total workers: 1,956,600 | ||
Employment by specific NAICS
There are a wide variety of jobs to be found in the automotive industry. Machines and humans work together, with machines helping, not replacing, humans. The heartbeat of any factory is the employees who perform the work. With close to 2,000,000 laborers performing specialized jobs, there are a multitude of different tasks performed.
Processes like forging, stamping, bending, forming, welding, machining, and assembling are all used to manufacture and maintain motor vehicles. All of these processes involve fabricating metal, which means our Metal Fabrication industry page is an excellent additional resource for automotive safety managers and workers.
On each sub-industry page, we highlight the specific activities that pertain to that particular automotive sector. Here are just a handful of the hundreds of activities performed across this industry.
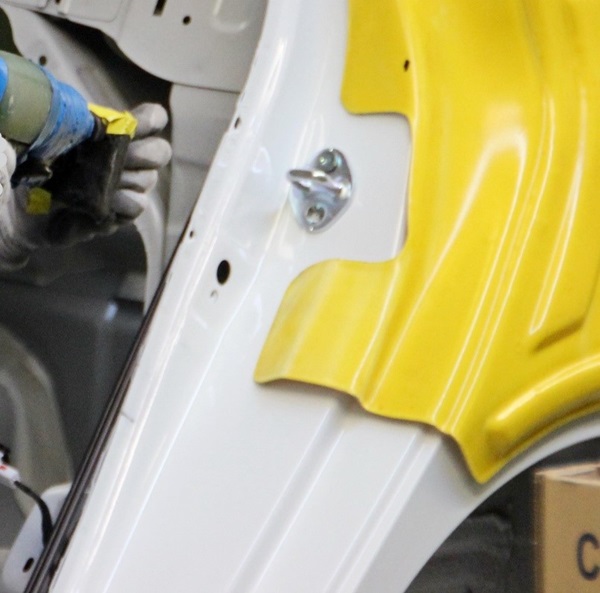
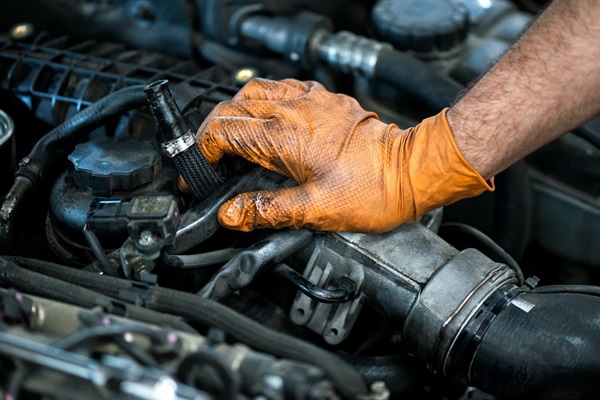
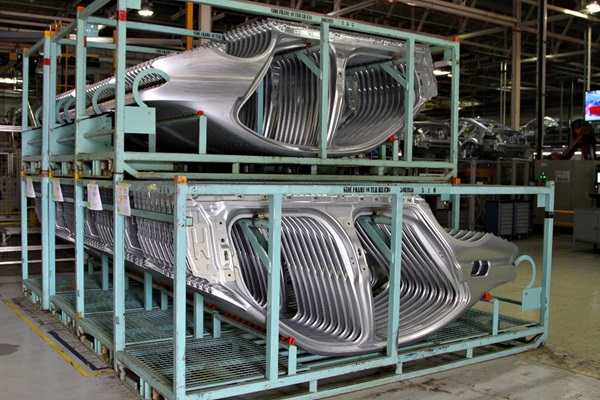
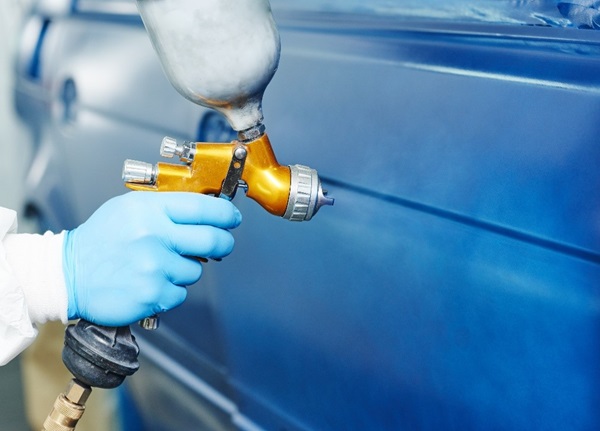





Assemblers in this industry put together various parts during subassembly work and final assembly to build parts and vehicles. You will find this worker assembling bolts, using many different types of tools, and moving heavy parts. They use tools, machines, and their hands.
Mechanics perform maintenance on a variety of automobiles. You will find this worker replacing defective mechanical parts, disassembling and reassembling equipment, and rebuilding components. These workers typically spend a lot of time using their hands are often working in an enclosed vehicle where they are exposed to contaminants.
Metalworkers are needed across the entire automotive industry, creating individual parts and repairing metal structures. You will find these workers welding, cutting, shaping, and forming metal pieces. Vehicles have metal everywhere across their bodies, which means a lot of metal must be shaped to the correct size.
Auto body workers repair damage caused by accidents or wear and tear. You will find this worker smoothing surfaces of objects, cutting materials, removing dents, and installing machine parts. They repair and refinish automotive vehicle bodies. These workers stand most of the time, spend a lot of time using their hands, and are exposed to many contaminants.
Every vehicle that drives off the assembly line is checked multiple times throughout the entire manufacturing process, ensuring quality standards are being met. You will find this worker checking parts, assembly work, collecting samples of materials for testing, and test-driving vehicles.
Automotive paint workers help paint the surface of vehicles and trailers. You will find these workers applying paint coatings, cleaning production equipment, and positioning work pieces. Because most motor vehicle paintlines are automated, over 70% of all workers are in repair shops where the process isn't automated.
Robots can't weld every spot on the vehicle, which means human welders are still needed. Auto parts manufacturing and trailer manufacturing are two of the largest industries for welders. You will find these workers welding components in flat, vertical, or overhead positions.
The entire automotive industry has many objects moving at all times. You will find this occupation loading docks, moving parts, moving materials to production areas, and moving finished vehicles to warehouses.
Assembly lines need a lot of materials and resources to keep running efficiently. You will find these workers supplying materials and handling tools, in addition to cleaning work areas and equipment. They also help hold materials and tools on the assembly line.
Die Setters set stamping presses found in automotive factories. You will find these workers aligning metal parts, making cut-resistant gloves a high priority for their safety.
Automotive factories have many machines that need to be maintained and repaired. A maintenance worker must be skilled in electricity, welding, and mechanical systems. You will find these workers repairing equipment and cleaning machines and machine parts. Cleaning solvents, oily parts, and metalworking fluids are a definite concern for these workers.
Some parts need to be specially fabricated and are needed in small numbers, which is where machinists come into play. You will find these workers replacing worn tools, sharpening dull cutting tools, and using cutter-grinding machines.
An automobile has at least four tires, which means a lot of rubber tires are needed for a vehicle to run. This worker operates machines to build tires. You will find these workers trimming excess rubber, cutting plies, and painting solvents.
A multitude of automotive parts are shaped to different dimensions. You will find these workers inspecting metal workpieces and operating machines such as lathes, cutters, and shears to make metallic and plastic workpieces.
Automotive parts are needed in all shapes and sizes, including rods and other structural shapes. You will find these workers operating machines to extrude or draw thermoplastic or metal materials into tubes, rods, hoses, wire, and bars.
Industrial Mechanics repair and maintain industrial production and processing machinery. You will find these workers cutting and welding metal to repair broken metal parts.
Many automotive parts components are molded. This is the worker that operates and works with metal/plastic molding, casting, and coremaking machines. They mold or cast metal or thermoplastic parts or products.
Running an automotive factory requires all construction trades to keep it operating. You will find these workers constructing structures and handling equipment and tools.
Dies are specialized tools used to cut and shape the material. They are mostly used in a press. This worker helps produce, maintain, and repair dies. They lay out metal stock, fit and assemble parts, and make and repair dies.
There is a multitude of electrical machines operating in the automotive industry. Electricians are the workers that install, maintain, and repair electrical wiring, equipment, and fixtures.
A vehicle requires tires to be occasionally changed once the tread wears down. You will find these workers remounting wheels, removing puncturing objects, and assisting mechanics.
Machines are operated to crush, grind, and polish materials. You will find these workers crushing and grinding materials, along with mixing chemicals.
The rubber used in tire manufacturing needs to be cut to exact lengths. These workers operate machines that cut/slice materials, such as glass and rubber.
Grinders use hand-held power tools to sand and polish metal surfaces. You will find these workers sharpening edges and corners on metal parts.
A trailer has metal components fitted across its entire frame. You will find these workers positioning welding parts and moving parts into position.
Automotive factories are laid out with heavy equipment and machinery designed to help workers. These workers install, dismantle, and move machinery and heavy equipment. You will find them adjusting bolts, positioning parts, using hand tools, and drilling holes.
Pipes run all across automotive factories. Plumbers are the workers that assemble, install, alter, and repair pipes that carry water, steam, air, and other liquids. They install mechanical control systems and hydraulic systems.
Automobile bumpers and grills are electroplated with a thick protective layer of metal. This helps the parts resist wear and corrosion. You will find this worker operating coating machines to coat metal or plastic products with chromium, zinc, copper, cadmium, or nickel to protect or decorate surfaces.
Crank shafts, drive shafts, axels, and numerous other automotive parts are die forged. You will find these workers removing dies, forging hammers, and moving metalwork pieces.
Lathes assist in cutting automotive parts such as brake discs, brake drums, hubs, and valves. You will find these workers replacing worn tools, sharpening dull cutting tools, and using cutter-grinding machines.
Several automotive structural body parts are produced from roll formed metal parts, such as panels. You will find these workers operating shears and grinders and adjusting machines.
The body of some trailers, such as camping trailers, are made with fiberglass. You will find these workers laminating layers of fiberglass on molds to form vehicles.
Engine parts and components are made from melted aluminum and other materials like zinc. This allows for the part to withstand years of wear and tear. You will find this worker operating heating equipment to temper, harden, anneal, or heat-treat metal or plastic objects.
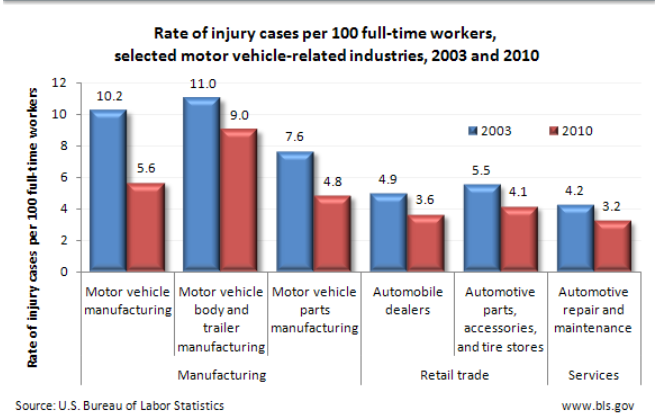
Performing work safely in the automotive industry is imperative, as injuries can occur at any time during the manufacturing and maintenance processes. The multitude of different tasks performed, whether in automotive shops, body shops, or on factory floors, require workers to wear PPE at all times.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) incident numbers shown below clearly indicate that safety measures must be a high priority for all workers. However, some automotive sub-industries need to be extra cautious. Trailer manufacturing and vehicle manufacturing are essentially twice as dangerous as all other U.S. automotive sub-industries.
| Sub-Industry | Total Recordable Cases for Every 100 Employees |
|---|---|
| Motor vehicle body and Trailer manufacturing | 6.9 |
| Motor vehicle manufacturing | 6.4 |
| Tire manufacturing | 3.8 |
| Motor vehicle parts manufacturing | 3.7 |
| Engine and engine parts manufacturing | 3.6 |
| Automotive repair and maintenance | 2.6 |
| Average for All U.S. Industries: 3.1 | |
Even though assembling cars is more technologically driven than ever before, worker
injuries are still a major concern. The good news is that incident rates have been coming down, as shown
in
the image below.
As we mentioned earlier, Elon Musk is quoted as saying, "Great companies are built on products!" Yes, we've won some awards over the years for some really cool new products, but ultimately, we know that it's you, the consumer, who determines which companies make great products. One thing we can say for certain is that the products our industry makes are great because they aid in keeping you from getting hurt.
At MCR Safety, we're dedicated to creating the very best PPE products. We want to see the above BLS injury stats keeping coming down, which ultimately means we're doing our part in bringing leading-edge PPE technology to market.
An automotive worker's most important tools are the ones he or she was born with: eyes and hands.
At MCR Safety, We Protect People!

Learn more about MCR Safety product features that protect against these common hazards.
Click "Learn More" to find info on protecting yourself against these hazards and find the right gear for the job.


 Why MCR Safety Products?
Why MCR Safety Products? 
MCR Safety manufactures and supplies Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Simply put, WE PROTECT PEOPLE! We are known world-wide for our extensive product line depth surrounding gloves, glasses, and garments spanning across numerous industries. We offer the total package of safety gear encompassing industrial gloves, safety glasses, protective garments, welding gear, industrial boots, Flame Resistant (FR) gear, face shields, and much more. From a glove standpoint alone, MCR Safety manufacturers and supplies over 1,000 different style gloves. Here are some of the many reasons MCR Safety is your go to source for PPE:
MCR Safety is recognized as a global manufacturer stretching across six countries, with both distribution and manufacturing facilities. Our core competency and specialty is manufacturing and supplying protective gloves, glasses, and garments. The information shown and provided on MCR Safety’s website, its safety articles, industry resource pages, highlighted hazards and safety equipment should be used only as a general reference tool and guide. The end user is solely responsible for determining the suitability of any product selection for a particular application. MCR Safety makes no guarantee or warranty (expressed or implied) of our products’ performance or protection for particular applications.