
"Enthusiasm is the engine of success."
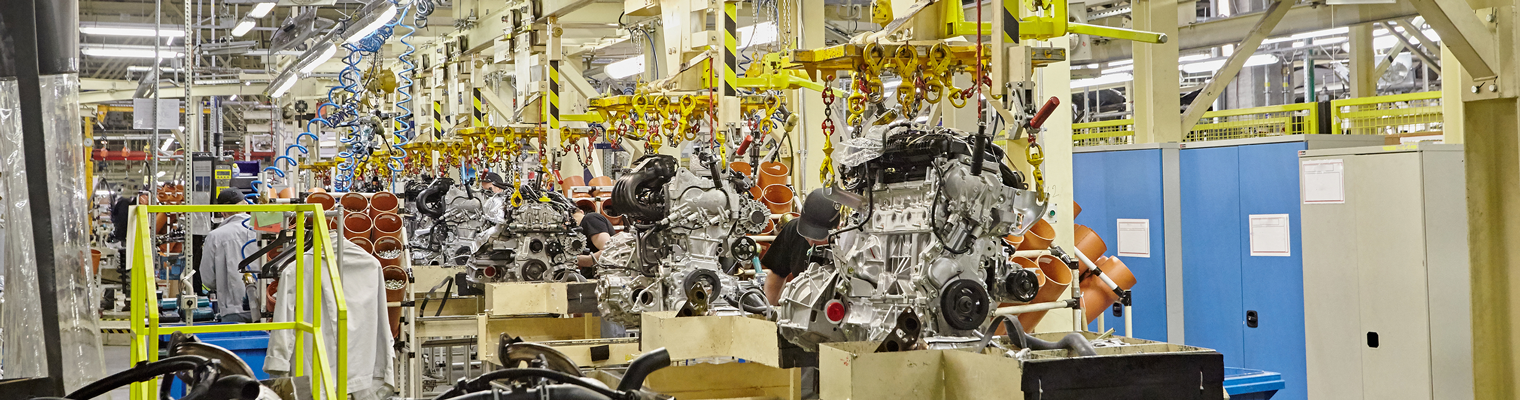
An engine is the heart of a vehicle's operating system and ultimately what makes the vehicle a successful form of transportation. Without the engine, a vehicle is just another big piece of stamped out metal appearing in various shapes and sizes.
In addition to being manufactured for vehicles, engines are also built for aircraft and large machinery equipment, such as Caterpillar excavators and dozers. They are also used in trailer manufacturing for the hydraulic systems.
Companies in the engine manufacturing industry manufacture and assemble diesel engines, electric engines, industrial engines, and natural gas-powered engines. The engines built will eventually be used as the workhorse for automotive vehicles, heavy-duty trucks, mid-duty trucks, and RVs.
We cover more below on which industries engines are built for, where the workers are located, and, most importantly, the PPE workers require when manufacturing engines. First, though, a little bit about the engine’s history, engine companies, and the industry’s economic impact.

A trailer's hydraulic system engine being assembled
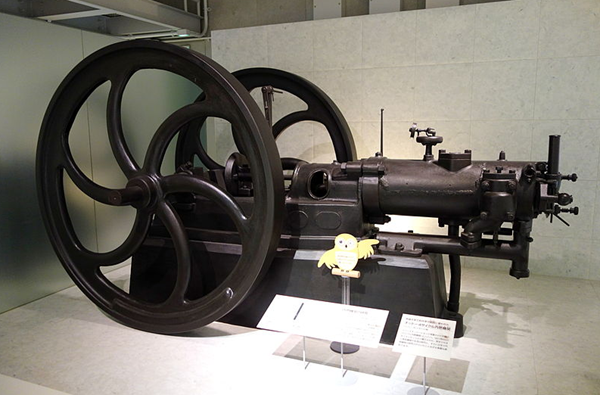
1876 four-cycle engine
The first successful four-stroke internal combustion engine was built in 1876 by Nicolaus Otto. His invention, called the “Otto Cycle Engine”, offered the first practical substitute to steam engine as a power source.
Combustion is the chemical process of releasing energy from a fuel and air mixture. The expanding combustion gases push the piston, which rotates the crankshaft. Then, through a system of gears in the powertrain, motion drives a vehicle’s wheels.
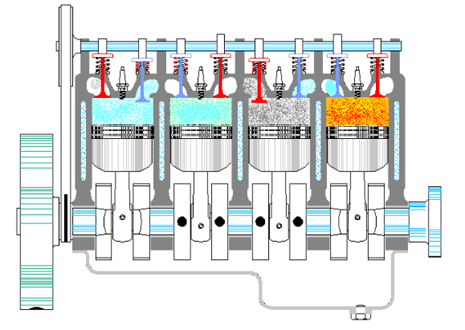
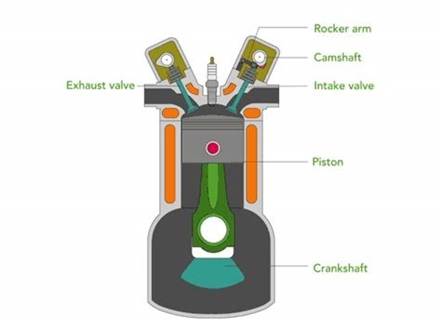
Throughout the 20th century, the two most common internal combustion engines manufactured were the diesel and petrol engines. Today, in the 21st century, electrical engines are starting to become mainstream with newer technology being introduced every day. This is an important point to mention, as PPE needing worn by employees must change within different manufacturing plants. Example being, workers that manufacturer electric engines are using thinner gauged metals and will need even higher levels of cut-resistant gloves.
Engines come in many different shapes and sizes, and are built for a multitude of different purposes. Here is a quick rundown of the different types of engines.
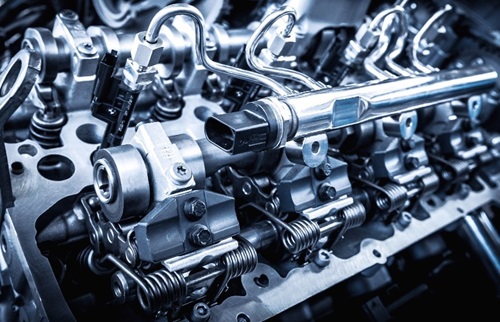
In this internal combustion engine, fuel is mixed with air and then inducted into the cylinder during intake. With fuel-air inside the engine, a spark ignites, causing combustion. Hot gases produced are used to drive the pistons.
This type of engine is the primary engine used in automobiles. Other applications for this engine include aircraft, motorcycles, motorboats, and small engines.
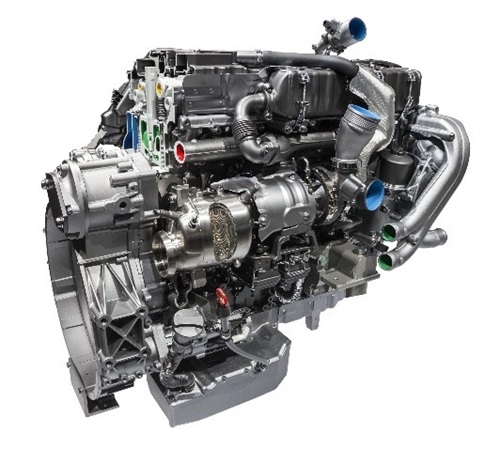

In this internal combustion engine, only air is inducted into the engine and then compressed. The diesel engine then sprays fuel into the hot compressed air, causing it to ignite.
Heavy-duty diesel engines are primarily manufactured for freight trucks, however, they may also be found in light- and medium-duty trucks. They are used for several purposes: heavy-duty transportation, medium-duty trucks, and for industrial machinery engines.
In 2017, there were roughly 900,000 diesel engines manufactured in the U.S.

Electric engines are powered by an electric current that generates a magnetic charge and turns the driveshaft. These engines utilize large lithium-ion batteries or batteries made with newer technologies.

An Electric Vehicle's Battery
There are two basic types of electric engine: all-electric vehicles (AEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs).
Ultimately, the global automotive engine & parts manufacturing industry is linked to motor vehicle production, as engines are the essential component of the automobile. The industry is forecasted to hit $299 billion in 2019.
Automotive engine & parts manufacturing involves making the following products: camshafts, crankshafts, engines, fuel injectors, pistons, valves, and pumps. With regard to this industry resource page, we highlight the manufacturing of engines, not all the components that make up this industry.
The engine and turbine industry is linked to more industrial production and is projected to reach $55billion in 2019.
Honda is the world’s largest engine manufacturer, producing more than 23 million units annually. Have you ever wondered who makes the best automotive engine? Well, Ranker knows the answer to that question, as over 81,000 people have voted on the topic. Honda is ranked the #1 engine by voters.
Many automotive companies manufacture engines in their own automotive plants. However, some treat the engine as they do other parts and source from outside suppliers. GM has sourced from others over the years, including Suzuki’s 3-cylinder portfolio, but have produced their engines more in-house in recent years.
Engine manufacturing goes beyond just the engines found in automotive vehicles. The Truck and Engine Manufacturers Association represents manufacturers of internal combustion engines. Their collection of members represents some of the largest industrial companies operating across the world.
| Member Companies That Are a Part of the EMA | |
|---|---|
| AGCO Corporation | INNIO |
| American Honda Motor Company, Inc. | Isuzu Technical Center of America, Inc. |
| Briggs & Stratton Corporation | Kawasaki Motors Corp., USA |
| Caterpillar, Inc. | Komatsu Ltd. |
| Cummins, Inc. | Kubota Engine America Corporation |
| Cummins Power Systems | MAN Truck & Bus AG |
| Daimler Trucks North America, LLC | MTU America, Inc. |
| Deere & Company | Navistar, Inc |
| DEUTZ Corporation | PACCAR, Inc |
| FCA US, LLC | Scania CV AB |
| Fiat Powertrain Technologies | Volkswagen of America, Inc. |
| Ford Motor Company | Volvo Group North America |
| General Motors Company | Wärtsilä North America, Inc. |
| Hino Motors Manufacturing USA, Inc. | Yanmar America Corporation |
Caterpillar, Cummins, and General Electric Company are three of the largest companies from this list. Here are some of the many areas where you will find industrial engines used:
As we mentioned above, engines serve a wide range of purposes.
The companies mentioned above manufacture a multitude of parts, with the engine block making up the core component. It is the main structure housing hundreds of parts allowing the engine to function properly.

Engine Block
The manufacturing of the engine block is primarily accomplished by sand casting. The reason for this is that the engine must be able to withstand the extreme pressure created when combustion occurs. Green sand molding casting is the process most widely used. This means it must withstand high temperatures and constant vibrations.
BMW’s video helps visualize what takes place during casting, a highly automated process.
The engine block, a one-piece component, is the single largest piece of metal in an automobile. It is where combustion converts into mechanical energy.
Here are the steps for manufacturing it:
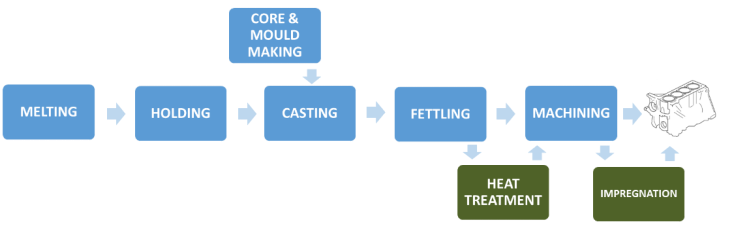
Aluminum is melted.
A sand mold is created from a mixture of zircon sand, glue, and hardener. The combination of materials come together to withstand the temperatures of molten metal and are used for only one casting.

Sand
A machine injects the mixtures mentioned above into a master mold made of iron. A base core is created that allows other cores to attach while traveling down an assembly line.
The base core travels down an assembly line and an additional 17 cores are added.
Molten cast iron, aluminum, or magnesium alloy is poured into the combined core molds.

Aluminum Pouring
Casted engine block spends six hours in the thermal sand reclaim oven. This breaks down the glue and allows the sand to fall away. Heat treatment of the block improves mechanical properties too.
Minor finishing of the engine is required and rough machining is performed.
Quality checks are performed.
Final machining takes place.
As you can imagine, working around heat and metal means MCR Safety gloves, made with DuPont Kevlar®, are an ideal choice for workers. Be sure to check out MCR Safety’s industry page on foundries for further casting information.

Once the engine block is manufactured, a working engine is only halfway complete. An engine consists of an assortment of mechanical and electronic components, all of which must be assembled into a working whole.
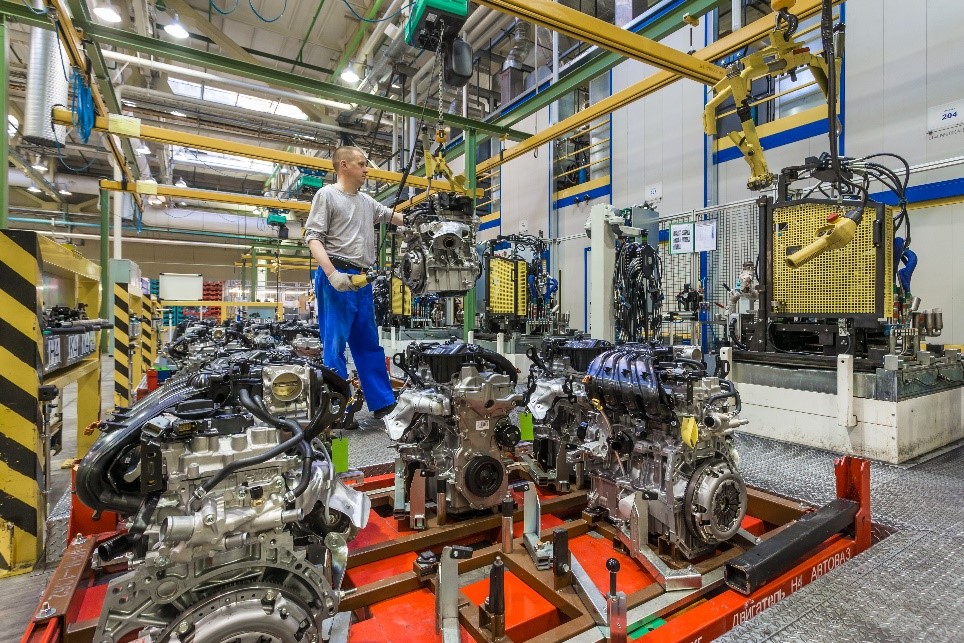
A robot is at the heart of most of this process, completing tasks like installing the pistons into the cylinder bores and attaching pistons to the crankshaft. However, the engine assembler still closes up the back of the engine block, tightens bolts, arranges wires, and moves the engine to the motor vehicle assembly line.
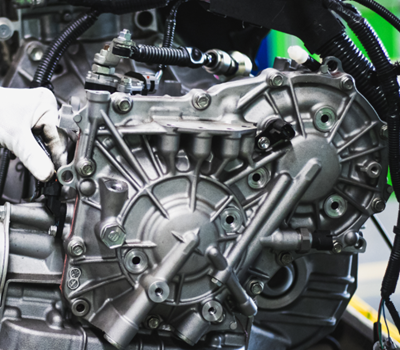
Engine Being Assembled
The U.S. Census Bureau last reported in 2016 that there were roughly 55,000 workers manufacturing gasoline engines. Here are the states where the 819 engine manufacturing companies are operating and where these workers are found.
When you examine only diesel engine manufacturing, there are thirteen states that are home to heavy-duty diesel engine manufacturing. North Carolina is one of those states, leading the way with the production of 327,500 diesel engines last year. Other key states include Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, and New York.
| State | Number of Manufacturers |
|---|---|
| California | 101 |
| Michigan | 80 |
| Ohio | 51 |
| Texas | 48 |
| Florida | 39 |
| Indiana | 34 |
| North Carolina | 31 |
| Illinois | 29 |
| New York | 29 |
| Missouri | 25 |
| Pennsylvania | 25 |
| Wisconsin | 23 |
| Tennessee | 21 |
| Ranking | State | Number of Heavy-Duty Diesel Engines |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | NC | 327,500 |
| #2 | IN | 160,985 |
| #3 | MI | 109,000 |
| #4 | OH | 70,000 |
| #5 | NY | 76,400 |
| #6 | MD | 40,000 |
| #7 | TX | 29,800 |
| #8 | IA | 28,750 |
| #9 | MS | 28,700 |
| #10 | GA | 12,700 |
| #11 | AL | 7,200 |
| #12 | UT | 1,600 |
| #13 | SC | 940 |
There are around 96,000 employees manufacturing industrial engines. Whether it’s an automotive engine or an industrial diesel engine being manufactured, many workers find occupations that provide employment. Here is a look at the occupations found in this industry.
Manufacturing engines, like most other automotive industries, requires assemblers that fasten piping, install wiring, and cut out parts. Many of the same occupations that make up the part manufacturing industry also work in this industry. However, we’re going to highlight the engine assembler.
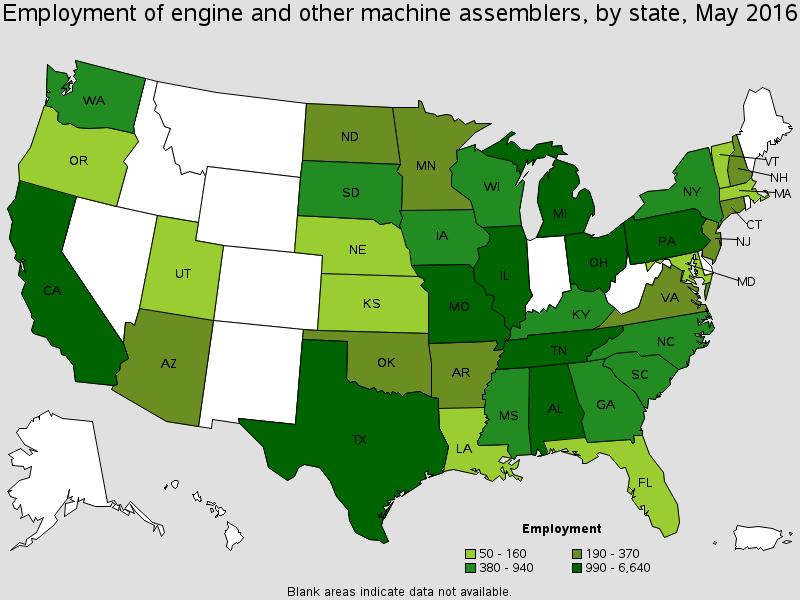
As you might already have guessed, where the automobiles are manufactured is where you will find most U.S. engines being manufactured. Here are the states employing the most engine assemblers.
| State | Employment |
|---|---|
| Ohio | 6,640 |
| Michigan | 4,850 |
| Texas | 2,190 |
| Illinois | 2,050 |
| Alabama | 1,530 |
| Industry | Employment |
|---|---|
| Automotive Parts Manufacturing | 13,430 |
| Engine, Turbine, and Power Transmission Equipment Manufacturing | 6,540 |
| Agriculture, Construction, and Mining Machinery Manufacturing | 3,780 |
| General Purpose Machinery Manufacturing | 2,550 |
| Aerospace Product and Parts Manufacturing | 2,110 |
Automotive parts manufacturing is where you find most engine assemblers.

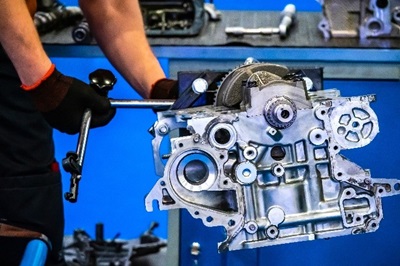
Many of the activities found in the automotive industry involve metal fabrication. Be sure to check out our Metal fabrication industry page for more information and resources.
What do 91% of engine assemblers say their work requires every day? If you guessed PPE, you would be correct. Compared to other automotive industries, manufacturing engines isn’t as dangerous as something like metal stamping; however, it still has more injuries than the overall industry average.
Manufacturing engines is about 16% more dangerous on average. It might be even higher if not for the fact that most of the engine manufacturing is an automated process. With that said, employees still come into contact with heat, abrasive sand, oil, sharp metal, and numerous other hazards.
At MCR Safety, We Protect People with state-of-the-art PPE. Let us keep you safe when you are manufacturing engines!

Find the right MCR Safety product that protects you against these common hazards.

Working around abrasive sand during casting, handling additives and assembling metal parts onto engines requires only the best abrasion resistant gloves. We make them form fitting to your hands, so you can efficiently assemble engine parts too!

Metal is all over an engine, which requires a worker’s arm protected at all times. We manufacture a wide range of cut resistant sleeves to keep your arms protected, including a new A9 cut-resistant sleeve.

Anyone working around hot castings, hot machine surfaces, and hot dies should consider gloves designed for heat protection. We’ve written a Heat Resistant Gloves blog to keep you informed!
Learn More About Contact Heat and Hot Objects Protection
Workers insert and place numerous lubricated parts to the engine. If not careful, parts can easily slip due to oils. We manufacture cut protection gloves designed for these oily applications.

Engine assemblers need to feel the components making up engines. Yet, at the same time, they need cut protection when working around metal, such as drilling holes in metal parts. We make some featherweight cut-resistant options you should consider wearing.
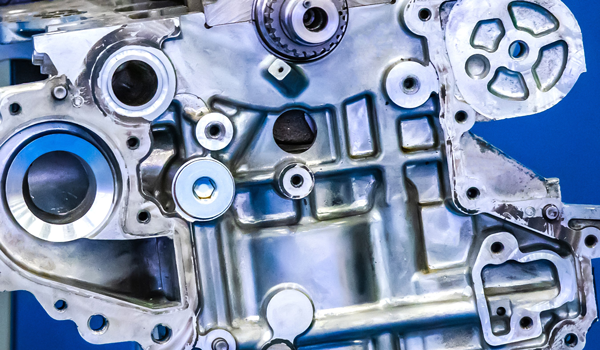
Casting flash, excess material that needs to be removed, and sharp edges on castings and dies are just a couple reasons workers need cut protection in this industry. Workers also need to be protected when handling knives, files, and pliers.
Common Applications:
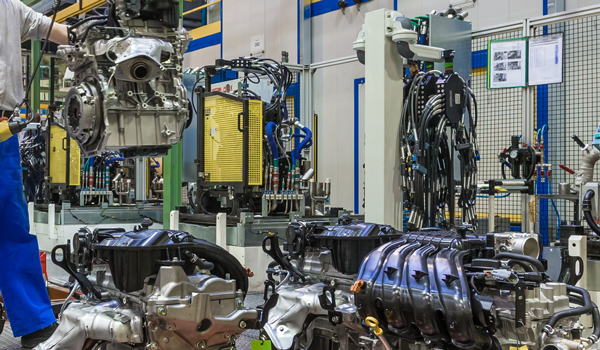
There some heavy parts that make up a completed engine. If you know your back up hand is going to get banged up, consider our cut and back-of-hand PPE styles. Wearing gloves with 360-degree protection makes a lot of sense.

Workers grind away excess metal found on the engine, meaning face shields, and safety glasses are definitely required at work. Plus, whenever hot molten metal is around during die casting, machine operators need eye protection. Furthermore, assemblers need protection from flying projectiles.

Grippaz disposable gloves come in hand when handling die lubricants and applying substances machines.
Common Applications:
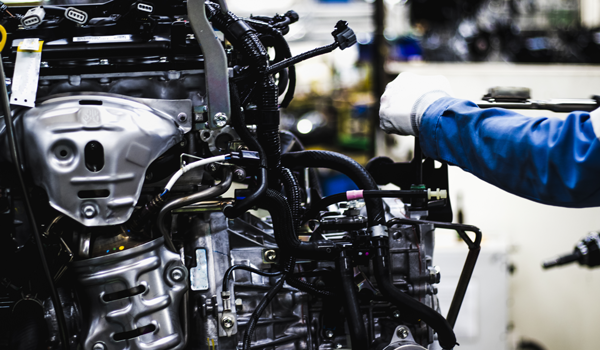
Assembling engines together into a functioning unit involve many components. Some workers only need general purpose protection, made with a PU dip that allows ultimate dexterity and feel.
Common Applications:

We now manufacture a Cut A9 apron for workers concerned with any hazards faced that may cut their front torso area. With hot metal found all across engine manufacturing, some workers may benefit from this advanced protection. It’s also rated ANSI 5 for contact heat!
Common Applications:
 Why MCR Safety Products?
Why MCR Safety Products? 
MCR Safety manufactures and supplies Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Simply put, WE PROTECT PEOPLE! We are known world-wide for our extensive product line depth surrounding gloves, glasses, and garments spanning across numerous industries. We offer the total package of safety gear encompassing industrial gloves, safety glasses, protective garments, welding gear, industrial boots, Flame Resistant (FR) gear, face shields, and much more. From a glove standpoint alone, MCR Safety manufacturers and supplies over 1,000 different style gloves. Here are some of the many reasons MCR Safety is your go to source for PPE:
MCR Safety is recognized as a global manufacturer stretching across six countries, with both distribution and manufacturing facilities. Our core competency and specialty is manufacturing and supplying protective gloves, glasses, and garments. The information shown and provided on MCR Safety’s website, its safety articles, industry resource pages, highlighted hazards and safety equipment should be used only as a general reference tool and guide. The end user is solely responsible for determining the suitability of any product selection for a particular application. MCR Safety makes no guarantee or warranty (expressed or implied) of our products’ performance or protection for particular applications.