

"Just because you can, doesn't mean you should."
There is no truer statement when it comes to working on a car. At some point, all automotive vehicles require maintenance and repair. That is just how the cookie crumbles, or, more aptly, how the tire blows. This inevitable need means, unless you have proper training, you should probably consider getting your vehicle serviced by trained professionals.
Whether you have a flat tire, need a part replaced, or require routine maintenance work, motor vehicles require upkeep. Repair and maintenance workers help repair automobiles, maintain vehicles, and bring vehicles back to working order.
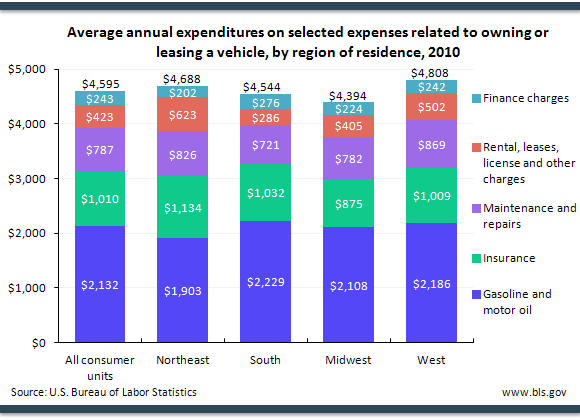
Maintaining and operating a vehicle is a part of any vehicle budget
The quality and reliability of automobiles have drastically improved over the past several decades. This means a greater number of older vehicles are still on the road, with mileage easily exceeding 100,000 miles in many cases. As a result, demand for automotive repairs has increased.
Below, we "look under the hood" and provide an in-depth look at the automotive repair and maintenance industry, the companies and workers, the activities, and, most importantly, the hazards these workers encounter.
In total, the automotive repair and maintenance industry generates around $838 billion a year for U.S. companies.
When the economy is good, people buy more new cars. Unfortunately, for this industry, that means less service and fewer repairs are needed. However, when the economy is struggling, consumers begin to hold back on purchasing larger ticket items, including cars. During slower economic periods, consumers look to repair their current vehicle over buying a brand new one.
You may be surprised by this, but in Cuba, there are cars still on the road that were built in the 1950s. How is this possible? Well, for one, Cuba has not had the free market system the U.S. has, where new cars can easily be purchased, so they’ve had to make the old ones last. Second, it is a testament to how auto mechanics and repairmen can fix cars and keep them going some 60-70 years after initial production. Think about that the next time you want to trade in your “old” car.

Vehicle from the 1950's still operating in 2017
Before we cover the occupations and activities in this industry, we first want to highlight the different types of shops. This is important because the PPE found in each will be slightly different. You will find a lot more welders in body shops than in paint shops, so it makes sense that this sub-industry requires more welding protection.
Companies within this sub-industry repair passenger cars, trucks, and vans. The industry is forcasted to hit $69 billion in 2019.
When a car requires repair, the first stop is to the mechanic. Mechanics are the technicians that actually diagnose and repair mechanical and electrical systems.
Mechanics work on a number of automotive systems, including engines, transmissions, and drive belts. In addition, the need to understand and be familiar with new electrical systems is on the rise, since more and more electric cars are being manufactured.
Types of repair include:


This sub-industry of automotive repairs refurbishes, refinishes, and replaces vehicle bodies and frames, windshields, and window glass.
When a vehicle suffers damage in an accident and requires repair from collisions, people turn to a body shop for assistance. Body repairers restore the structural integrity of car frames and bring them back to life. The repairs required after a collision are more substantial than what mechanics can provide.
The industry had $47 billion in total revenue in 2018. As long as Americans drive metal, fiberglass, or carbon fiber automobiles, this industry will continue to exist.
Paint shops repair scratches, scuffs, dents, and bodies of motor vehicles. First, the exterior of the damaged car is fixed and then the paint is applied, which gets your vehicle looking new again.
Unlike the automated paint process found in motor vehicle manufacturing, the spray paint process is a time-consuming process done in paint shops. It involves filling, sanding, and cleaning the body panels before spraying them by hand. Many times, all a vehicle needs is a fresh coat of paint.


You can’t drive a car safely with a busted window, which means drivers turn to those specializing in glass repair to get them back on the road.
Automotive body and glass repairers use many tools, ranging from plasma cutters to pneumatic tools, and “classic” tools like pliers, wrenches, hammers, and screwdrivers. This group of workers also has one of the highest injury rates of all occupations. They often experience minor injuries, such as cuts, burns, and scrapes.
Types of repair include:
This sub-industry of automotive repair involves companies engaged in changing motor oil and lubrication fluids in the chassis of vehicles. Annual revenue in this sub-industry comes in at around $5.5 billion.
Major U.S. companies specializing in oil and lubrication include Havoline Express, Jiffy Lube, and Pennzoil.

Most auto mechanics and body shops are likely to be small companies, operating in an independent garage and in a specific geographic location. Many of them compete based on the quality of their work, their reputation, and their price. With that said, there are also some large national companies competing in this market space.
The following is a list of some of the largest companies within this industry.
| Company | Employees |
|---|---|
| Firestone | 40,000 |
| Pep Boys | 18,000 |
| Safelite Group, Inc. | 12,501 |
| Auto Club Group | 8,000 |
| Caliber Collision | 7,700 |
| Mister Car Wash | 7,500 |
| Valvoline International, Inc. | 6,700 |
| Jiffy Lube | 6,539 |
| Monro Muffler/Brake | 6,157 |
| Service King Collision Repair | 4,680 |
Demand looks strong for automotive repairs, as all machines break sooner or later. There are more cars on the road today than ever before, which is understandable since worldwide production of vehicles has been climbing over the past 30 years. This means that more cars will need service at some point, which in turn means there is a need for more and more workers in this industry.
Yet, even with an increased demand for mechanics and technicians, the supply of qualified technicians has not kept up. The shortage of technicians is starting to affect this industry at a time when vehicles are loaded with tons of advanced technology.
Even with a shortage, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) eports high levels of employment for each NAICS in this sub-industry, which speaks to the overall volume of repairs taking place. Automotive repair and maintenance jobs employ around 928,000 workers. Body shops employ around 275,000 workers.
Here is a closer look at employment in the different types of shops:
| Automobile dealers | 31% |
| Automotive mechanical and electrical repair and maintenance | 27% |
| Self-employed workers | 13% |
| Automotive Parts, accessories, and tire stores | 9% |
| Other | 20% |
There are roughly 749,000 auto service technicians in the U.S., representing the largest segment within NAICS 81111. The above table shows the primary areas where they are found working.
| Automotive body, paint, interior, and glass repair | 57% |
| Automobile dealers | 19% |
| Self-employed workers | 9% |
| Automotive mechanical and electrical repair and maintenance | 6% |
| Other | 9% |
There are roughly 160,000 body shop repairers in the U.S. The above table shows the primary areas where they are found working.
| Automotive body, paint, interior, and glass repair | 87% |
| Self-employed workers | 4% |
| Construction | 2% |
| Automotive parts, accessories, and tire stores | 2% |
| Other | 5% |
There are roughly 19,600 automotive glass installers and repairers in the U.S. The above table shows the primary areas where they are found working.
Here is a look at the occupations found in this industry.
Cars and their technology are changing at an alarming rate. This means that automotive repair workers find themselves operating in a challenging work environment and must undergo continuous training to learn the new technology. The top three occupations found in this industry are the following:
A wide variety of career opportunities are available. Here's a look at the various jobs found in this automobile industry.
Lubricate machines, change parts, and perform machinery maintenance. The automotive repair industry employs over 445,000 of these workers. You will find these workers cleaning machines and machine parts. Cleaning solvents, oil, and metalworking fluids are a definite concern for these workers. Common job titles for this position are Lubricator, Maintenance Man, and Oiler.
Repair or overhaul mobile equipment, such as cranes, bulldozers, graders, and conveyors used in construction. There are roughly 8,000 of these workers found in repair and maintenance.. You will find these workers replacing worn parts and reassembling equipment using hand tools. Common job titles for this position are Heavy Equipment Technician, Field Mechanic, and Equipment Mechanic.
Repair automobiles, trucks, buses, and other vehicles. There are roughly 34,000 of these workers in automotive repair. You will find this worker replacing defective mechanical parts, disassembling and reassembling equipment, and rebuilding components. Technicians commonly specialize in air-conditioning, brakes, and transmissions. Work is typically performed in an enclosed vehicle, where workers are exposed to contaminants, and they spend a lot of time using their hands. Common job titles for this occupation are Automotive Service Technician, Master Technician, and Mechanic.
Replace defective mechanical parts, disassemble and reassemble equipment, and rebuild components. There are roughly 22,000 of these workers in automotive repair. They repair automobiles, trucks, buses and other vehicles. These workers are typically in an enclosed vehicle, are exposed to contaminants, and spend a lot of time using their hands. Common job titles for this occupation are Automotive Service Technician, Master Technician, and Mechanic.
Around 153,000 of these workers help move material and vehicles in automotive repair. That is a large number of hands needing to be protected. You will find these workers operating conveyors, transporting materials, and operating machines. Common job titles are Laborer and Operator.
Move materials, objects, and stock. There are over 150,000 of these workers in automotive repair. Machine feeders also fall into this worker group. Common job titles for this position are Line Tender, Laborer, and Materials Handler. Due to the use of one’s hands in these jobs, wearing gloves is necessary.
Wash and clean vehicles and machinery. There are over 149,000 of these workers in automotive repair. You will find this worker connecting hoses, installing parts, and removing debris. These workers use materials such as water, cleaning agents, and hoses. Common job titles for this occupation are Auto Detailer and Car Washer.
Repair and refinish automotive vehicle bodies and straighten vehicle frames. There are over 101,000 of these workers in automotive repair and maintenance. You will find this worker smoothing surfaces of objects, cutting materials, removing dents, and installing machine parts. They repair and refinish automotive vehicle bodies. These workers stand most of the time, spend a lot of time using their hands, and are exposed to many contaminants. Common job titles for this occupation include Auto Body Man, Auto Body Repair Technician, Body and Frame Man, Body Man, and Body Technician.
Apply paint coatings, clean production equipment, and position work pieces. There are roughly 27,000 of these workers in the automotive repair industry. They paint and coat surfaces. These workers are exposed to many contaminants. Common job titles for this occupation are Painter and Spray Painter.
Polish work pieces, mix ingredients, and operate painting equipment. There are roughly 27,000 of these workers in the automotive repair industry. They operate machines to paint the surfaces of automobiles, buses, trucks, trains, boats, and airplanes. These workers are exposed to many hazardous conditions and to many contaminants. Common job titles for this occupation are Automotive Painter, Finish Painter, and Paint Technician.
Repair and overhaul buses, trucks, and diesel engines. There are around 23,600 of these workers in automotive repair. You will find these workers dismantling heavy equipment, grinding parts, and lubricating equipment. These workers spend a lot of time using their hands to feel objects and use tools. Common job titles for this occupation are Bus Mechanic, Fleet Mechanic, Mechanic, and Truck Mechanic.
Replace and repair broken windshields and window glass in automobiles. There are roughly 18,000 workers in this sector of automotive repair. You will find this worker replacing vehicle glass, painting surfaces, and adjusting vehicle components. These workers are exposed to sharp broken glass and need great hand dexterity for removing screws and bolts. Common job titles for this job occupation are Auto Glazier, Glass Installer, Glass Technician, and Windshield Installer.
Supply or hold materials, in addition to cleaning work areas and equipment. There are around 16,000 of these workers in the automotive repair industry. You will find these workers attaching cables, changing machine gears, and handling a lot of material. All of these activities make gloves extremely important. Common job titles for this position are Laborer, Press Helper, and Material Handler.
Repair and replace tires. There are roughly 7,000 of these workers in the automotive repair industry. You will find these workers remounting wheels, removing puncturing objects, and assisting mechanics. Common job titles for this occupation are Service Technician, Tire Buster, and Tire Technician.
Clean facilities and treat facilities/surfaces with protective substances. There are roughly 4,800 of these workers in automotive repair. You will find this worker applying and releasing chemical solutions/toxic gases, along with setting traps to kill or remove pests. These workers are exposed to outdoor weather and contaminants. Common job titles are Pest Control Technician and Pest Technician.
Keep buildings in clean and orderly condition. There are roughly 4,800 of these workers found in the automotive repair industry. You will find this worker performing heavy-duty cleaning or simply cleaning snow/debris from sidewalks. Common job titles are Cleaner, Custodian, and Janitor.
Keep machines, mechanical equipment, or the structure of an establishment in repair. There are around 2,800 of these workers in the automotive repair industry. You will find these workers pipe fitting, repairing equipment, and repairing buildings. Job titles for this position are Maintenance Worker, Maintenance Mechanic, and Facilities Manager.
Operate machines designed to cut, shape, and form metal. There are roughly 2,100 employees found in this occupation in the automotive repair industry. You will find these workers fabricating metal products, lifting heavy materials, and working with their hands. Common job titles for this position are Sheet Metal Worker and Welder.
Assemble finished products and parts. There are around 1,200 of these workers in automotive repair. You will find this worker assembling bolts, using many different types of tools, and moving heavy parts. They construct finished products and the parts that go into them. These workers use many tools, machines, and, most importantly, need their hands protected. Common job titles for this occupation are Assembler and Fabricator.
Use hand welding, flame-cutting, hand soldering, and brazing equipment to weld/join metal components and to fill holes, indentations, or seams of fabricated metal products. There are around 1,000 of these workers employed in the automotive repair industry. You will find these workers welding components in flat, vertical, or overhead positions. Common job titles for this position are Maintenance Welder, Mig Welder, and Welder/Fabricator.
Operate welding, soldering, or brazing machines that weld, braze, or heat treat metal products. There are around 1,000 of these workers found in the automotive repair industry. You will find these workers adding material to work pieces, joining metal components, and annealing finished work pieces. Common job titles for this position are Fabricator, Mig Welder, Spot Welder, Fitter-Welder, and Braze Operator.
Perform tasks involving physical labor. There are roughly 1,000 of these workers in automotive repair. They operate hand and power tools of all types. You will find these workers preparing sites, digging trenches, erecting scaffolding, applying paint to surfaces, applying sealants, and assembling structures. Common job titles for this occupation are Helper, Laborer, and Skill Laborer.
With such a large workforce found in this industry, there are a multitude of different work activities requiring PPE to safely perform the job at hand. Here are some activities in each occupation that are performed regularly:




Many of the activities found in the automotive industry involve metal fabrication. Be sure to check out our Metal fabrication industry page for more information and resources.
Body shop work involves sharp metal and engines that have exposed parts. Both environments are hazardous to those working in an enclosed area like a garage or repair shop. The story of Steve Godziszewski reinforces this point and reminds us why mechanics must always wear proper protection. One day, a battery cable caught his fingernail and tore it off, eventually causing some of his finger to be removed. Today, he wears gloves every time he works on a car.
Don’t let the low number of injuries per worker fool you. Yes, there are only 2.6 injuries for every 100 employees. However, there are 1,300,000 workers in this entire industry, which means there are close to 33,000 people injured each year in automotive repair and maintenance.
| Industry | NAICS | # of Injuries |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive repair and maintenance | 8111 | 2.6 |
Working safely and wearing proper PPE is critical to reducing the number of work-related injuries. And, a nice pair of gloves keeps hands free from of all the dirt and grease encountered when repairing an engine or transmission.
At MCR Safety, We Protect People! That protection starts by first arming you with knowledge about the industry’s hazards and the PPE that will keep you safe. Hopefully, we’ve shed some light on this industry.

You take care of cars and the people driving them. Now, let MCR Safety take care of you and keep you safe at work!
Find the right MCR Safety product that protects you against these common hazards.

Body shop workers and maintenance workers handle a lot of rough, used material. They require abrasive-resistant gloves.

Chemical-resistant gloves and goggles should always be worn when cleaning parts, especially when working around HEPTANE and PROPANOL. Be sure to check out our permeation guide for specific chemical permeation breakthrough times.
Learn More About Automotive Parts Washer Protection
Auto mechanics and technicians work around a lot of oil and hazardous chemicals, including replacing harmful liquids in engine parts. These hazardous chemicals and liquids may be battery acid, sulfuric acid, heat transfer fluids, hydraulic fluid, coolants, fuel solvents, gasoline, additives, or hot oil. Check out our Chemical Permeation Guide for specific chemical breakthrough times.
Learn More About Chemicals and Liquids Protection
Anytime you're working around winches, pulling chains and mechanical components, there a high risk of injury. Moving equipment and spinning tools are always a safety concern. Guarding your fingertips and knuckles while working in confined spaces or around moving parts makes a lot of sense. Check out our Impact Protection page for additional information.
Learn More About Crush and Impact Protection
Working around gearboxes and transmission parts involves oily and greasy environments. Repair mechanics will need excellent protection from oily parts and metalworking fluids when machining parts.

Sanding a vehicle generates dust, as does sweeping, grinding, and cutting metal. We've got a wide selection of lined eyewear styles.

Hoses whipping under pressure will damage one's eyes rather quickly. Be sure you're wearing the proper PPE anytime you are using shop tools.

Compressed gasses, sparks, and combustible materials are found throughout an auto body repair shop.

Extremely hot auto parts require gloves designed for heat protection. We test for heat protection in our ITC lab.
Learn More About Heat Burns and Hot Objects Protection
Working in the service pit exposes a mechanic to falling objects. In addition, auto mechanics are routinely metalworking and rebuilding engines. Brake dust, chemical splashes, flying metal shavings, and sparks are real concerns for automotive body workers.

Removing and replacing engine parts increases the risk of hand injuries.

Automobile bodies are painted using organic solvents in the preparation of surfaces, such as cleaning, degreasing, and pickling. You're going to want to keep it out of your eyes.

Pinching is always a concern when working around a tire machine. Having some knuckle guards will keep your main tool protected: your hands.

Nicks and cuts from twisted metal are the norms in this job. Mechanics work around sharp edges and frequently use a lot of dangerous tools that can potentially cause deep lacerations, cuts, and scrapes.

Hand tools are used in every repair and maintenance job. Injuries can quickly occur to the hand when operating any tool.

Harmful substances such as spray paint may cause dermatitis, an inflammation of the skin.

Welders need shaded eyewear when cutting or grinding and when exposed to searing rays. Be sure to check out our Welding Protection page for more information.
Learn More About UV Radiation Protection
Welding is an essential process in body shop work. There is always a risk of burns and coming into contact with hot objects when you are a welder. Be sure to check out our Welding Protection page.
Learn More About Welding and Cutting Protection
Welding, grinding and cutting creates one of the greatest hazards faced in automotive repair and maintenance, whether that is fusing steel pieces on new cars or repairing old cars. We offer cut-resistant liners in several of our leather welding styles. Be sure to check out our Welding Protection page for more information.
Learn More About Welding Sharp Objects Protection
Sparks can burn through cotton or synthetic work shirts, causing the material to combust. With leather welding gear, you've got the protection needed when welding on a car's body. Be sure to check out our Welding Protection page for more information.
Learn More About Welding Sparks Protection Why MCR Safety Products?
Why MCR Safety Products? 
MCR Safety manufactures and supplies Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Simply put, WE PROTECT PEOPLE! We are known world-wide for our extensive product line depth surrounding gloves, glasses, and garments spanning across numerous industries. We offer the total package of safety gear encompassing industrial gloves, safety glasses, protective garments, welding gear, industrial boots, Flame Resistant (FR) gear, face shields, and much more. From a glove standpoint alone, MCR Safety manufacturers and supplies over 1,000 different style gloves. Here are some of the many reasons MCR Safety is your go to source for PPE:
MCR Safety is recognized as a global manufacturer stretching across six countries, with both distribution and manufacturing facilities. Our core competency and specialty is manufacturing and supplying protective gloves, glasses, and garments. The information shown and provided on MCR Safety’s website, its safety articles, industry resource pages, highlighted hazards and safety equipment should be used only as a general reference tool and guide. The end user is solely responsible for determining the suitability of any product selection for a particular application. MCR Safety makes no guarantee or warranty (expressed or implied) of our products’ performance or protection for particular applications.