

“Black stones...which burn like logs”

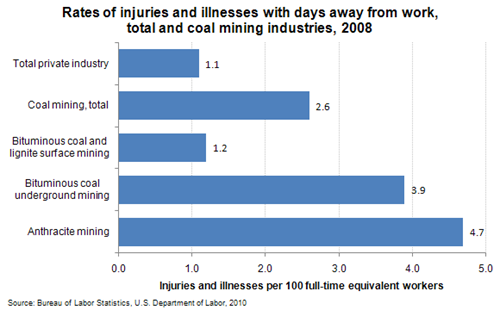
Marco Polo was one of the first Europeans to see and describe coal being used in China during his Asian travels. Since Polo’s travels in the 13th century, this burning coal log has kept countless people warm during cold, frigid months. However, when it pertains to actual coal mines, there is a dark side and it goes beyond the actual darkness found inside underground mines. According to the BLS, a coal miner is twice as likely to be injured when compared to the private industry. When you look specifically at underground mining, a worker is four times as likely to be hurt.
Hot working conditions, limited visibility, falling roofs, rock bursts, vehicle collisions, explosions from methane gas, dust and numerous other hazards are serious concerns for a coal miner.
In addition, there is always the possibility of being trapped, like the 33 Chile miners who were trapped for 69 days back in 2010. The good news is that safety injuries have drastically come down over the past 40 years. Since 2007 alone, the rate of injuries has dropped from 4.3 to 2.6 for every 100 employees.
MCR Safety is doing our part by constantly innovating safety gear that matches the needs of coal miners. Max 6 Anti-Fog technology is a new innovation the coal industry has embraced, due to its 6X greater AF dissipation properties. With flying particles all around, there is great risk for miners taking eyewear off due to fogging. With the Max 6 PD1210PF D4 dust rated goggle, coal miners no longer need to remove their safety gear! Check out our Max 6 page for more on this technology.
We cover all the coal mining hazards more in depth below. First though, lets cover a little more of the coal industry.
Greek philosopher Aristotle once referred to coal as a charcoal like rock. Well, he was not far from the truth. Coal is the fuel powering our modern day electrical power plants. It produces the needed steam to drive the massive turbines responsible for creating electricity. Ever since the creation of the steam engine and the Industrial Revolution, coal has served as the fundamental building block for our modern world.
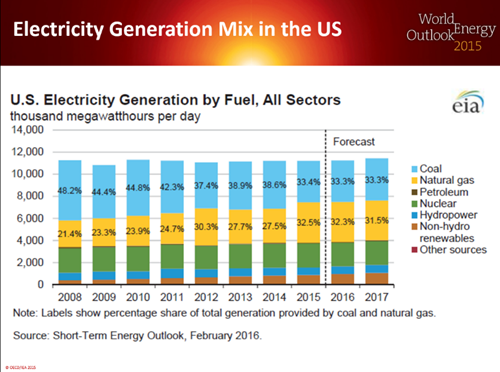
Mix of Electricity Generation
The two mining methods used in coal extraction are surface “Open Pit” mining and Underground mining. Simply put, surface mining is peeling back the earth and collecting coal near the surface. Whereas, underground mining requires tunneling and building shafts. The mining method chosen by companies depends on the coal deposit being extracted. The deeper the mine goes, the more hazards workers face.
The continuous mining method, an innovation from the late 19th and 20th century, eliminates the drilling and blasting operations found in conventional mining. This method uses a machine called a continuous miner. It continually extracts the coal, while loading onto a conveyor system.
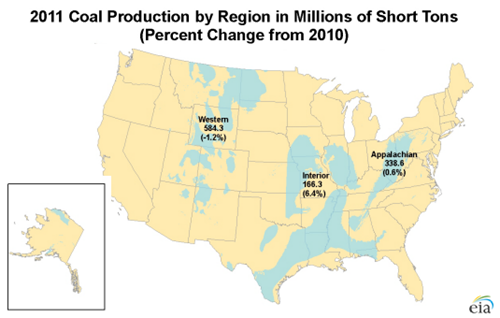
Coal Production Regions
Because of automated techniques, today’s miner has definitely changed with the times. Here is a look at 21st Century occupations found in the coal mining industry:
Click an occupation to expand and learn more.
Tend conveyors or conveyor systems that move materials or products to and from stockpiles, processing stations, departments, or vehicles. There are roughly around 600 of these workers found in Coal Mining. You will find these workers loading materials, clearing jams, and removing damaged materials. Common Job titles for this position are Chipper Operator, Flumer, Process Operator and Strapper Operator.
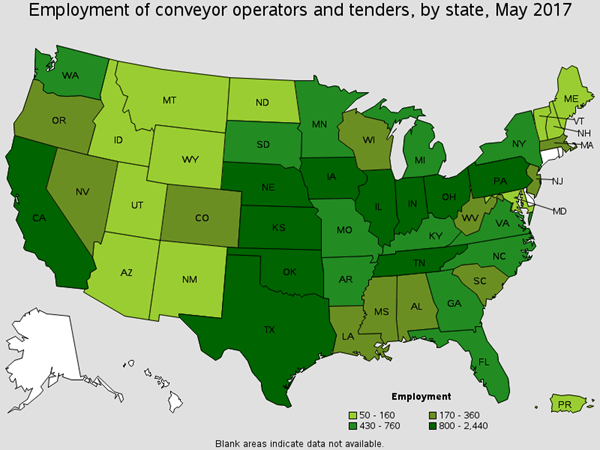
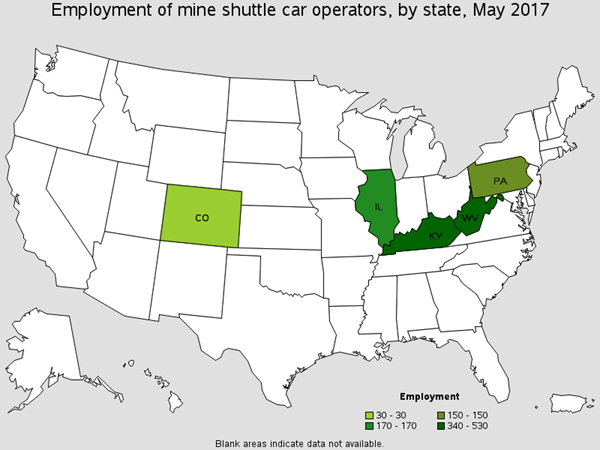
Employment of Conveyor Operators and Tenders by State
Perform tasks involving physical labor at construction sites. Mining examples include earth drillers, blasters and explosives workers, derrick operators, and mining machine operators. There are roughly around 22,000 of these workers found in Coal Mining. You will find these workers using hand tools, repairing drilling equipment, and transporting materials. Common Job titles for this position are Coal Miner, Mining Technician, Underground Miner, Helper, Laborer, Post Framer, and Construction Worker.
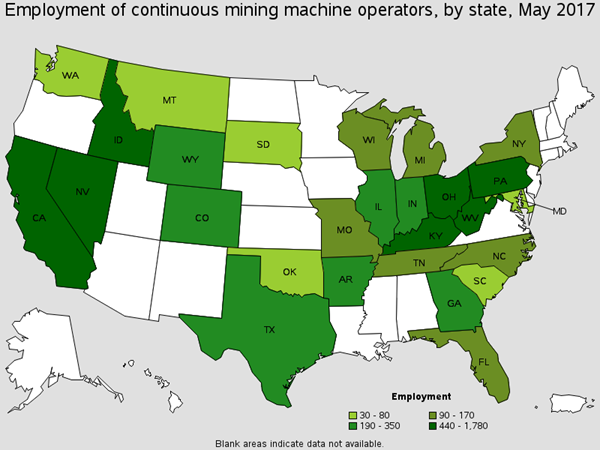
Operate mining machines that rip coal, metal and nonmetal ores, rock, stone, or sand from the mine face and load it onto conveyors or into shuttle cars. There are roughly around 3,500 of these workers found in Coal Mining. You will find these workers assisting in construction activities, checking the roof stability and cleaning equipment. Common Job titles for this position are Bore Mine Operator, Miner Operator, and Continuous Miners.
Operate dredge to remove sand, gravel, or other materials in order to excavate and maintain navigable channels in waterways. There are roughly 4,000 of the workers found in Coal Mining. You will find this worker operating equipment, tools and gauges. Common Job titles for this position are Dredge Operator and Dredger.
Install, maintain, and repair electrical wiring, equipment, and fixtures. Around 2,200 of this occupation found in Coal Mining. You will find these workers connecting wires to breakers and transformers, making dielectric and FR safety gear important. Common Job titles for this position are Industrial Electrician, Journeyman Electrician and Wireman, and Maintenance Electrician.
Operate machinery equipped with scoops, shovels, or buckets, to excavate and load loose materials. There are around 3,000 of these workers in the Coal Mining industry. You will find these workers breaking rock and operating power shovels. Common job titles for this occupation are Pit Operator, Loader Operator, and Dragline Oiler.
Help craft workers by supplying equipment, cleaning areas, and repair drilling equipment. Extraction craft workers are earth drillers, blasters and explosives workers, derrick operators, and mining machine operators. There are around 10,000 of these workers. Common Job titles for this position are Blasting Helper, Miner Helper, and Driller Helper.
Repair overhaul mobile mechanical, hydraulic, and pneumatic equipment. Examples of this equipment includes cranes, bulldozers, graders, and conveyors. There are around 2,800 of these workers found in Coal Mining. You will find these working replacing worn parts and reassembling heaving equipment with tools. Common Job titles for this position are Heavy Equipment Technician, Field Mechanic, and Mobile Heavy Equipment Mechanic.
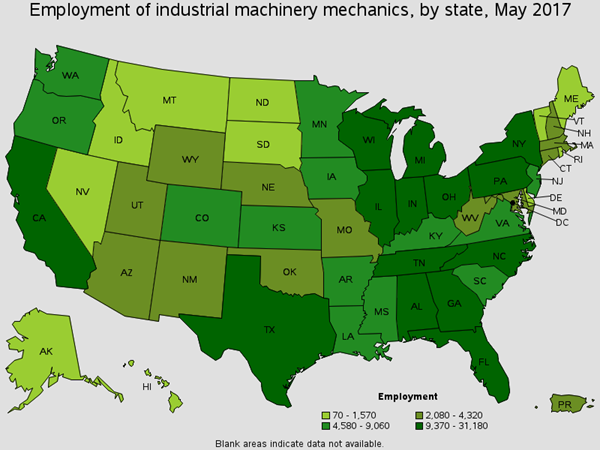
Worker activities include repairing, installing, and adjusting industrial machinery. Around 1,000 of this occupation works in Coal Mining. You will find these workers cutting and welding metal to repair broken metal parts. Job titles for this position are Fixer, Industrial and Master Mechanic.
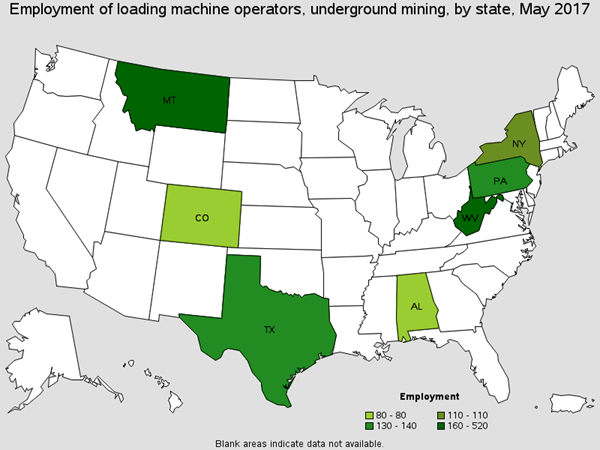
Operate underground loading machine to load coal, ore, or rock into shuttle / mine car or onto conveyors. There are around 1,000 of these workers are found in Coal Mining. You will find these prying off loose material from roofs, cleaning hoppers, and cleaning spillage. Common Job titles for this position are Miner, Production Miner, Shuttle Car Operator, and Under Ground Miner.
Operate machines designed to cut, shape and form metal. There are roughly 600 employees found for this occupation. You will find this worker fabricating metal products, lifting heavy material and working with their hands. Common job titles for this position are sheet metal worker and welder. Be sure to check out our Metal Fabrication industry educational page.
Keep machines, mechanical equipment, or the structure of an establishment in repair. There are around 8,500 of this occupation working in Coal Mining. You will find these workers pipe fitting, repairing equipment, and repairing buildings. Job titles for this position are Maintenance Worker, Maintenance Mechanic, and Facilities Manager.
Help move steel and other materials. Around 10,000 of these workers help move steel and other material across in Mining. That is a large number of hands needing protected. You will find these workers operating conveyors, transporting material, and operating machines. Common job titles are laborer and operator.
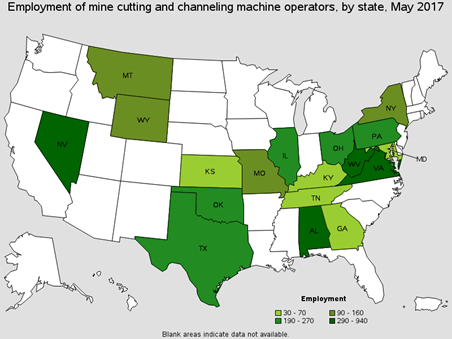
Operate machinery such as longwall shears, plows, and cutting machines to cut or channel along the face or seams of coal mines, stone quarries, or other mining surfaces to facilitate blasting, separating, or removing minerals or materials from mines. There are roughly around 1,700 of these workers found in Coal Mining. You will find these workers positioning roof supports, preventing cave-ins and cutting entries between rooms. Common Job titles for this position are Bore Miner Operator, Underground Miner and Shear Operator.
Operate diesel or electric-powered shuttle cars in underground mines to transport materials from working face to mine cars or conveyors. There are roughly around 1,300 of these workers found in Coal Mining. You will find these workers attaching drill bits and drill rods.. Common Job titles for this position are Coal Haul Operator and Shuttle Car Operator.
Repair, or overhaul mobile equipment, such as cranes, bulldozers, graders, and conveyors, used in construction, logging, and surface mining. There are roughly around 2,800 of these workers found in Coal Mining. You will find these workers replacing worn parts and reassembling equipment using hand tools. Common Job titles for this position are Heavy Equipment Technician, Field Mechanic, and Equipment Mechanic.
Operate machinery to install roof support bolts in underground mine. There are around 2,700 of this occupation working in coalmines, essentially the majority of this entire occupation. You will find these workers pulling down loose rock, drilling holes and positioning machines. Job titles for this position are Bolt Man, Bolter, and Underground Miner.
Operate welding, soldering or brazing machines that weld, braze, or heat treat metal products. The mining industry employs around 620 of these workers in coal mining. You will find these workers adding material to work pieces, joining metal components, and annealing finished work pieces. Common Job titles for this position are Fabricator, Mig Welder, Spot Welder, Fitter-Welder, and Braze Operators.
Use hand-welding, flame-cutting, hand soldering, and brazing equipment to weld/join metal components, fill holes, indentations, or seams of fabricated metal products. There are around 600 of these workers employed in coal mining. You will find these workers welding components in flat, vertical or overhead positions. Common Job titles for this position are Maintenance Welder, Mig Welder, and Welder/Fabricator.
Even though the work has changed over the years, safety hazards and injuries still occur. The chart to the right shows the most common nonfatal injuries in the coal industry.
As mentioned above, the hazards coal miners face are endless. A safe working environment ensures workers return home unharmed, while also creating a productive and profitable mining operation. We’ve got you covered with gloves, glasses, and garments needed in today’s coal mine. After all, keeping people protected is what we do. Let MCR Safety help protect you the next time you enter a mine!
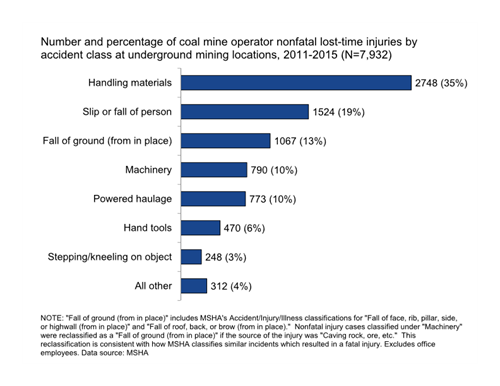
Nonfatal lost-time injuries
Find the right MCR Safety product that protects you against these common hazards.

Numerous mining injuries occur from working around low roofs, confined spaces, shoveling, lifting, and climbing. We have highly abrasive gloves for this very reason.

Cleaning mining equipment, working in processing plants, working around cutting oils and spray from leaking equipment are all concerns for the mining industry.

Impact in confined spaces, impact from crush and other mining equipment, heavy tool handling, falling rocks, tire changing, using grinding equipment and loading materials can all be hard on the back of a worker’s hands.
Learn More About Crush and Impact Protection
Mining underground and tearing into the earth is just a little dirty at times. Mining coveralls for underground mines and raingear for outdoor surface mining are absolute necessities.
Learn More About Dirt, Grime, and Fluids Protection
Many workers drive equipment in mining operations. Many mining fatalities occur due to Haul-Truck accidents. Drivers should not even second-guess wearing premier leather driver gloves.
Learn More About Operator Grip Protection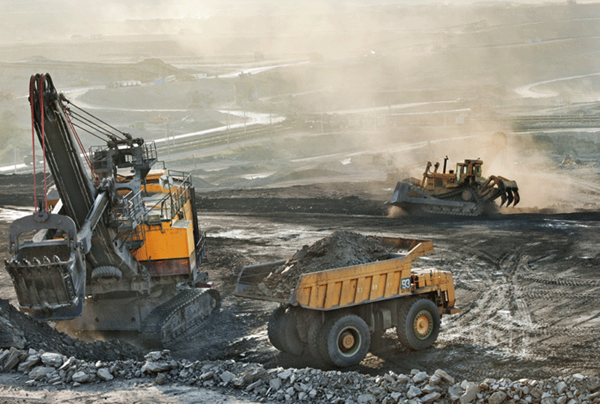
Dirt and dust are virtually in all mining environments. Drilling, blasting, and dust generated from hauling trucks are dust creators. Dust is known as one of the top on-the-job health risks of mining.
Learn More About Dust Protection
Mines require a lot of electricity, electrical wires and electrical panels. ARC Flash protection is the solution.
Learn More About Electrical Maintenance Protection
Mine sites use a lot of heavy trucks, hydraulics, conveyors, bulldozers and equipment. Mechanics need excellent abrasive grip and many times require back-of-hand protection.

Reinforced leather gloves are essential gear for miners.

Breaking up rock, drilling, and mining the earth creates flying particles. Grinding residues are present too. Check out eyewear designed for this exact scenario.
Learn More About Impaired Vision Protection
Lifting moderately heavy objects can quickly scrape up your hands. Material handling injuries are one of the leading causes of injuries for miners.
Learn More About Material Handling Protection
Underground mines are known for being dark and surface mines involve many moving vehicles. High-visibility jackets, vests and reflective coveralls are a must!
Learn More About Overall-Visibility Protection
Underground mining environments are often very hot and humid. We manufacture safety gear that incorporates breathable fabrics!

Working in a surface mine means the sun is probably directly hitting you. UV protective eyewear and bright shirts are the ticket.
Learn More About UV Radiation Protection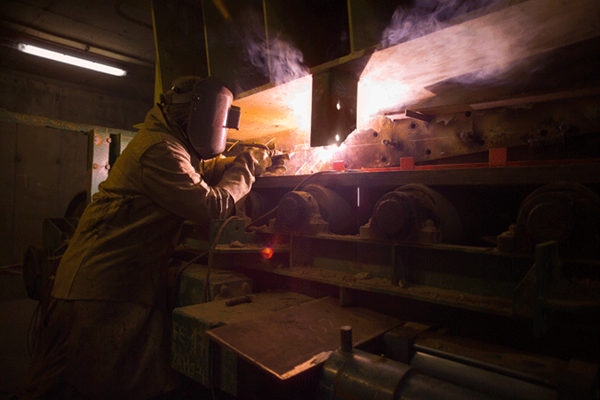
Installing steel borehole casings down a borehole requires welding at the joints. Face Shields and welding gear is essential mining gear.
Learn More About Welding Protection Why MCR Safety Products?
Why MCR Safety Products? 
MCR Safety manufactures and supplies Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Simply put, WE PROTECT PEOPLE! We are known world-wide for our extensive product line depth surrounding gloves, glasses, and garments spanning across numerous industries. We offer the total package of safety gear encompassing industrial gloves, safety glasses, protective garments, welding gear, industrial boots, Flame Resistant (FR) gear, face shields, and much more. From a glove standpoint alone, MCR Safety manufacturers and supplies over 1,000 different style gloves. Here are some of the many reasons MCR Safety is your go to source for PPE:
MCR Safety is recognized as a global manufacturer stretching across six countries, with both distribution and manufacturing facilities. Our core competency and specialty is manufacturing and supplying protective gloves, glasses, and garments. The information shown and provided on MCR Safety’s website, its safety articles, industry resource pages, highlighted hazards and safety equipment should be used only as a general reference tool and guide. The end user is solely responsible for determining the suitability of any product selection for a particular application. MCR Safety makes no guarantee or warranty (expressed or implied) of our products’ performance or protection for particular applications.