

"I believe in the dignity of labor, whether with head or hand; that the world owes no man a living but that it owes every man an opportunity to make a living."
In 1870, Rockefeller founded the Standard Oil Company, which would become the single largest refinery in the world. During the 1900's, a time when electricity was reducing overall crude oil demand, John D. Rockefeller envisioned automotive industry's demand for gasoline and transformed the Oil and Gas industry into what it is today.
The refining industry, also known as Downstream, encompasses companies engaged at manufacturing, refining and marketing petroleum products. Refineries chemically process, transport and sell refined products made from crude oil. Essentially, refining operations transform crude oil into functional products such as gasoline, fuel oils, and petroleum-based products; with the majority involving transportation fuels.
In 2012, the Census Bureau reported 801.4 billion in total shipments from US petroleum refineries. Operations are found across 30 states. However, roughly 44% of all US refineries are located along the Gulf Coast, with Texas operating 47 and Louisiana operating 19 refineries. Another 18 refineries are found in California.
| 2002 | 2007 | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Establishments | 203 | 195 |
| Value of Shipments ($ Millions) | 193,547 | 580,020 |
| Annual Payroll ($ Millions) | 4,324 | 6,359 |
| Total Employment | 61,585 | 64,839 |
| Value of Shipments per Establishment ($1,000) | 953,435 | 2,974,461 |
| Value of Shipments per Employee ($1,000) | 3,143 | 8,946 |
| Value of Shipments per $ of Payroll ($) | 44.76 | 91.21 |
| Payroll per Employee ($) | 70,212 | 98,079 |
| Employees per Establishment | 303.37 | 332.51 |
| Value of Shipments per Capita ($) | 673 | 1,925 |
| Population per Establishment | 1,416,873 | 1,544,775 |
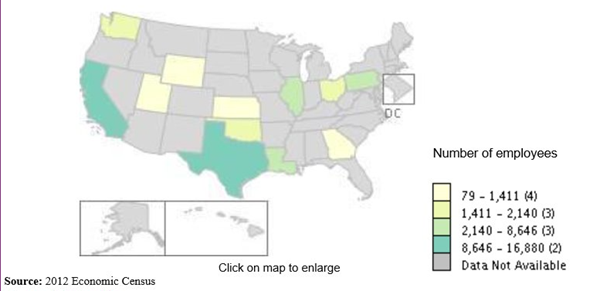
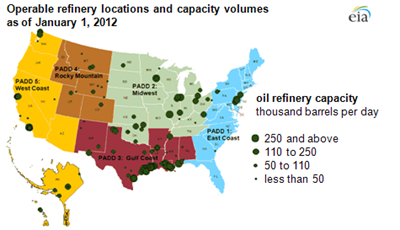
Operating refineries across the US
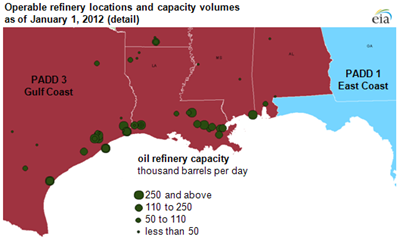
Texas and Louisiana Refinery Locations
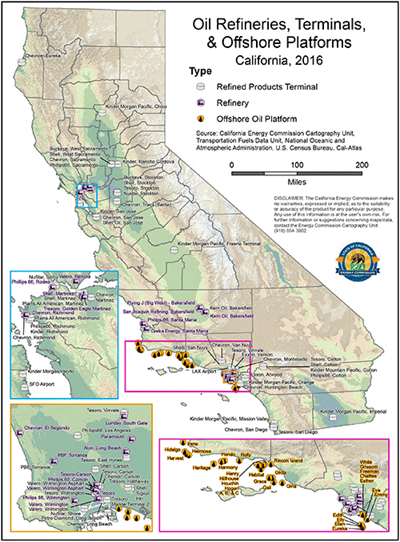
West Coast and Rocky Mountain Refinery Locations
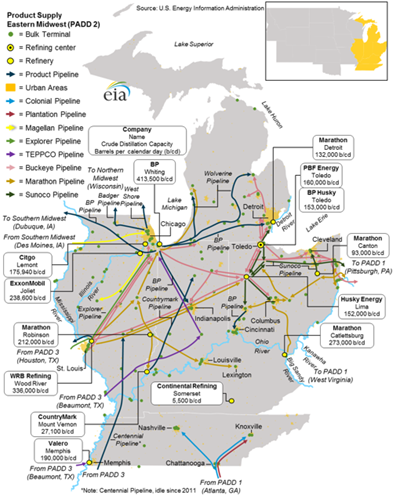
Eastern Midwest
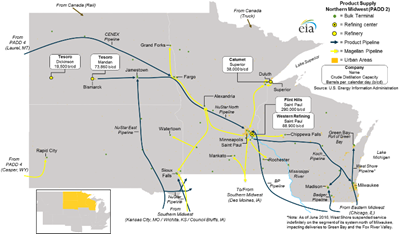
Northern Midwest
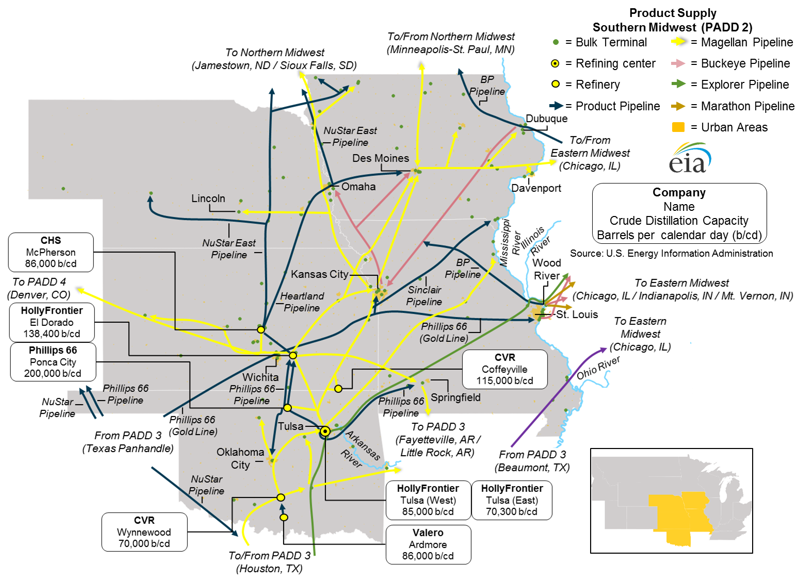
Southern Midwest
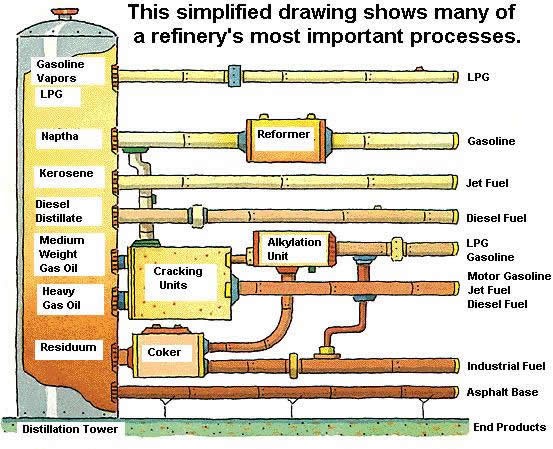
Crude oils are mixtures of thousands of different compounds called hydrocarbons. For oils to become products people user every day, refinery operations are needed. When converting crude oil, refineries use heat and pressure to separate out the final products. Here is the three-step process all refineries utilize:
Here is a look at each one of these processes:
Involves piping crude oil through hot furnaces. Fractionation is the separation process of oil into different portions, according to the boiling point, called fractions. The below distillation unit images highlight crude oil being separated out at different boiling ranges.

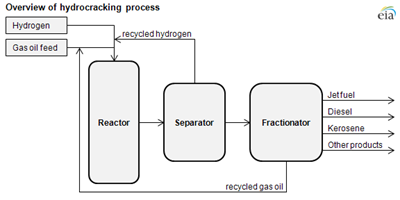
Hydrocracking Conversion Process
Cracking is the most common conversion refining process for breaking down larger and heavier hydrocarbon molecules into simpler and lighter ones.

Treatment Facilities
Finishing touches occur during final treatment and any unwanted contaminants are removed from the product.
Petroleum refineries transform crude oil into various petroleum products, from fuels for transportation, to heating oils and plastics. Here is a quick look at the many products refineries create:
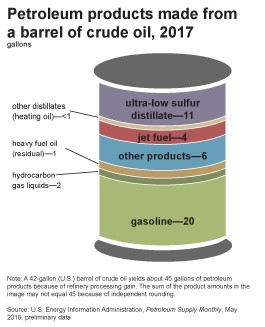
A barrel of crude oil produces roughly 20 gallons of gasoline, 12 gallons of distillate fuel, and 4 gallons of jet fuel.
Liquid Petroleum Gas, Gasoline, Naphtha

Kerosene. Jet Fuel, Diesel Fuel

Fuel Oils. Lubricating Oils. Asphalt and Tar, Petroleum Coke.
Synthetics, Rubber, Plastic and Pesticides
Once a refinery has transformed the final product, the final job is not complete. The final product must still arrive at its final destination. Here is a look at the flow of oil and gasoline after it has been refined:
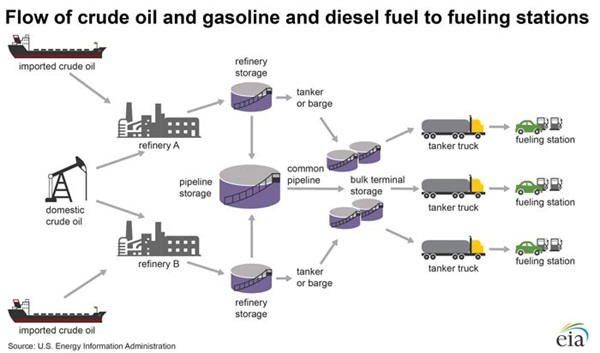
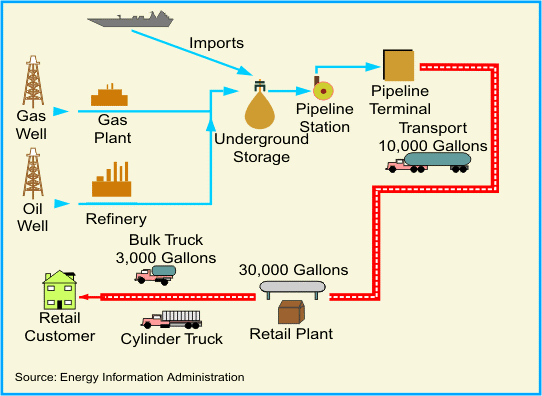
| Company | Total Employees |
|---|---|
| Exxon Mobil Corporation | 69,600 |
| Chevron Corporation | 51,900 |
| Marathon Petroleum Corporation | 43,800 |
| Mobil Corporation | 41,500 |
| BP America Inc | 22,100 |
| Shell Petroleum Inc. | 22,000 |
| ConocoPhillips | 16,900 |
| Andeavor | 14,300 |
| Carlisle Companies Incorporated | 12,500 |
These refiners are unique because they have no upstream facilities, only service stations.
| Company | Total Employees |
|---|---|
| Suncor | 12,000 |
| Valero | 10,015 |
As of January 2018, the below represents the 10 largest US refineries.
| Rank | Corporation | Company | State | Site | Barrels per calendar day |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saudi Aramco | Motiva Enterprises LLC | Texas | Port Arthur | 603000 |
| 2 | Marathon Petroleum Co LP | Marathon Petroleum Co LP | Texas | Galveston Bay | 571000 |
| 3 | ExxonMobil Corp | ExxonMobil Refining and Supply Co | Texas | Baytown | 560500 |
| 4 | Marathon Petroleum Corp | Marathon Petroleum Co LP | Louisiana | Garyville | 556000 |
| 5 | ExxonMobil Corp | ExxonMobil Refining and Supply Co | Louisiana | Baton Rouge | 502500 |
| 6 | PDV America Inc | Citgo Petroleum Corp | Louisiana | Lake Charles | 418000 |
| 7 | BP PLC | BP Products North America Inc | Indiana | Whiting | 413500 |
| 8 | ExxonMobil Corp | ExxonMobil Refining and Supply Co | Texas | Beaumont | 365644 |
| 9 | Chevron Corp | Chevron USA | Mississippi | Pascagoula | 352000 |
| 10 | WRB Refining LP | WRB Refining LP | Illinois | Wood River | 336000 |
Here is a look at the top occupations found across this industry and the above top 10 US refineries: (Click an occupation to expand and learn more.)
Assemble finished products and parts. There are around 1,300 of these workers in the Oil Refining industry. You will find this worker assembling bolts, using many different types of tools, and moving heavy parts. They construct finished products and the parts that go into them. These workers use alot of tools, machines, and most importanly need their hands protected. Common job titles for this occupation are Assembler and Fabricator.
Operate equipment to control chemical changes or reactions in the processing of industrial products. There are around 2,000 of these workers in the Oil Refining industry. You will find this worker adding treating agents to products, cleaning production equipment and draining pump water. Common job titles are Operator and Technicians.
Operate entire chemical processes or system of machines. Around of 1,400 of these workers are in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers operating chemical processing equipment, collecting samples and testing chemicals. Common job titles for this position are Chemical Operator, Process Operator, and Vessel Operator.
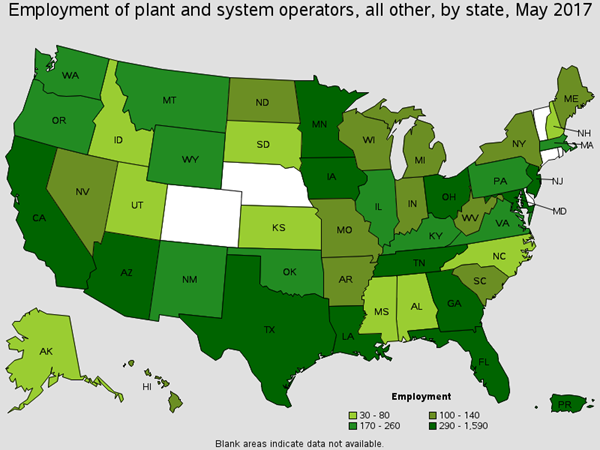
Employment of Chemical Plant and System Operators
Conduct qualitative and quantitative chemical analyses or experiments in laboratories for quality and process control. There are around 1,000 of these workers in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers analyzing chemical compounds, conducting quality control tests and maintaining technical equipment. Common job titles for this position are Scientist and QC Chemist.
Perform tasks involving physical labor at construction sites. There are roughly around 8,600 of these workers found in the Oil Refining Industry. You will find these workers using hand tools, repairing drilling equipment, and transporting materials. Common job titles for this occupation are helper, Laborer, Post Framer, and Construction Worker.
Operate machines to crush, grind, and polish materials. There are roughly around 4,800 of these workers found in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers mixing chemicals, collecting materials and using picks. Common Job titles for this position are Batch Mixer, Fabricator, and Miller.
Install, maintain, and repair electrical wiring, equipment and fixtures. There are around 1,400 of these workers in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers connecting wires to breakers and transformers, making dielectric and FR safety gear important. Common Job titles for this position are Industrial Electrician, Journeyman Electrician and Wireman, and Maintenance Electrician.
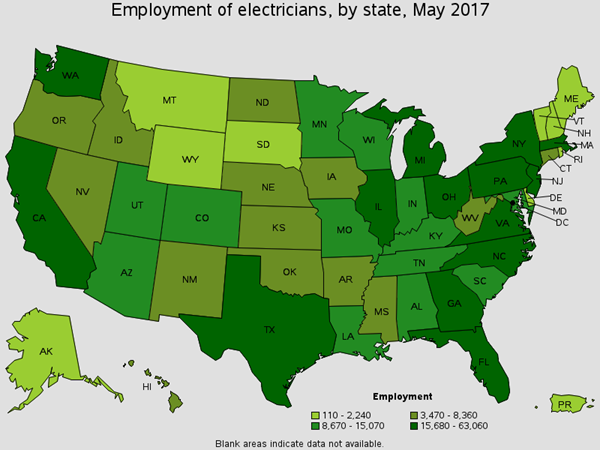
Employment of Electricians
Operate or tend heating equipment other than basic metal or plastic processing equipment. There are around 500 of these workers in Oil Refining. You will find these workers handling, moving objects and clearing equipment jams. Common Job titles for this position are Dry Kiln Operator, Dryer Feeder, and Overn Operator.
Worker activities include repairing, installing, and adjusting industrial machinery. There are around 4,600 of this occupation working in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers cutting and welding metal to repair broken metal parts. Job titles for this position are Fixer, Industrial and Master Mechanic.
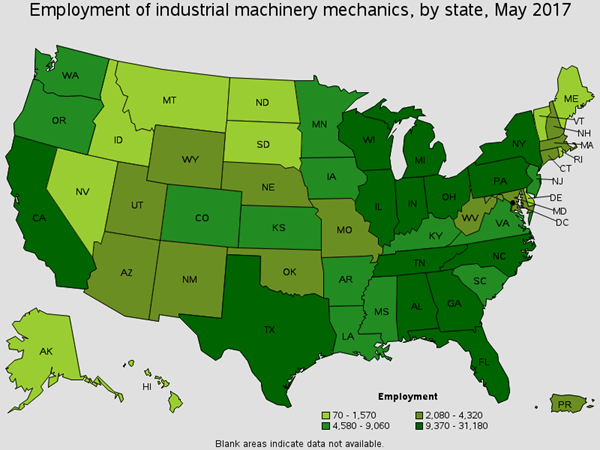
Employment of Industrial Machinery Mechanics
Lubricates machines, changes parts, and performs machinery maintenance. Oil Refining operatoins employ a little over 10,000 of these workers. You will find these workers cleaning machine and machine parts. Cleaning solvents, oil and metalworking fluids are a definite concern for these workers. Common Job titles for this position are Lubricator, Maintenance Man, and Oiler.
Machinists are the workers who utilize the machine and cutting tools. This occupation is highly skilled at operating machinery. There are around 1,200 of this occupation working in the Oil Refining industry. You will find this worker operating machine tools to produce precision parts. Job titles for this position Gear Machinist, Machine Operator and Maintenance Machinist.
Operate machines designed to cut, shape and form metal. There are roughly 2,800 of these workers in Oil Refining operations. You will find these workers fabricating metal products, lifting heavy materials and working with their hands. Common job titles are Sheet Metal worker and Welder. Be sure to check out our Metal Fabrication industry educational page.
Operate machines to mix or blend materials. There are around 4,600 of these workers in OIl Refining operations. You will find these workers mixing substances to create chemical solutions, measuring ingredients and moving objects. Common job titles are Blender, Machiner Operator, and Mixer.
Collect data on work environments for analysis . Implement programs designed to limit chemical, physical, biological, and ergonomic risks to workers. There are 880 of these workers in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers testing workplaces for chemical hazards, maintaining personal protective equipment and monitoring use of safety equipment. Common job titles for this position are Safety Professional, Safety Specialist, and Safety EHS leader.
Operate machines preparing products for storage or shipment. There are around 1,400 of this occupation working in the Oil Refining Industry. You will find these workers inspecting products and removing packaged items. Job titles for this position are Machine Operator, Packaging Operator, and Fabrication Technician.
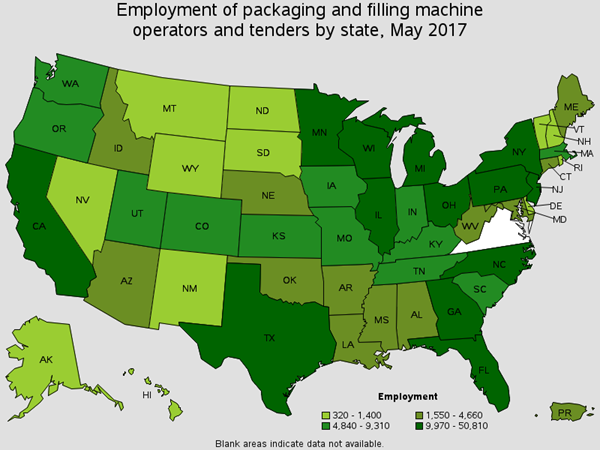
Employment of Packaging and Filling Machine Operators
Operate equipment used for applying concrete, asphalt, or equipment used for tamping gravel, dirt, and other materials. There are around 1,100 of these workers in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers operating machines, cleaning machines, and spreading concrete or other aggregate mixtures. Common job titles are Operator, Paver Operator, and Roller Operator.
Operate petroleum refining or processing units. There are around 20,000 of these workers in the Oil Refining Industry. You will find these workers monitoring gauges, opening valves to regualte the flow of oil, and operating manifold/pumping systems. Common Job titles for this position are Gauger, Head Operator, Pumper, and Refinery Operator
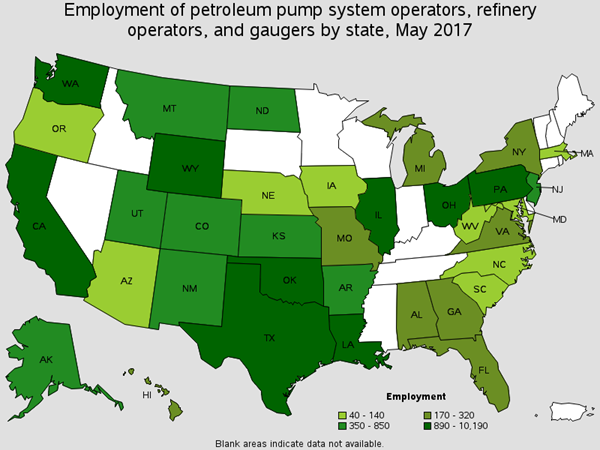
Employment of Petroleum Pump System Operators
Assemble, install, alter, and repair pipelines. There around 700 of these workers in Oil Refining. You will find these workers hammering pipes, securing pipes, and cutting piples. Common job titles for this position are Pipe Fitter, Pipe Welder, and Steamfitter.
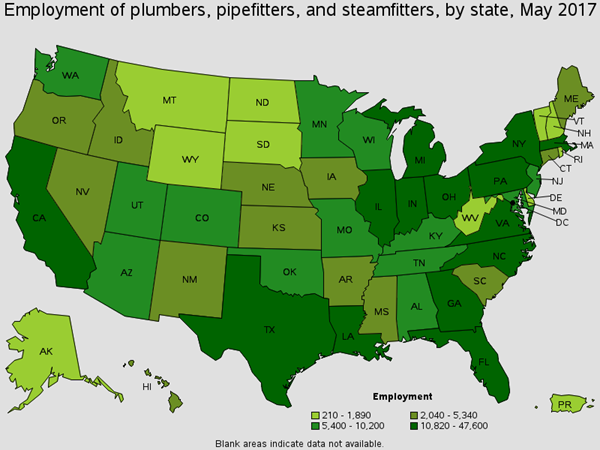
Employment of Pipelayers, Plumbers, Pipefitters, and Steamfitters
Operate a variety of drills to remove underground oil and gas. They also remove core samples for testing during oil and gas exploration. There are around 540 of these workers in Oil Refining. You will find this worker connecting sections of dril pipe, operating drilling equipment, and raising drill pipes. Common job titles for this occupation are Drill Operator, Driller, and Oil Rig Operator
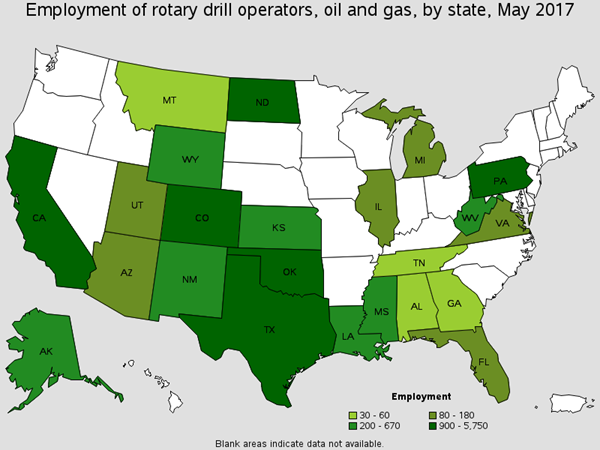
Employment of Rotary Drill Operators, Oil and Gas
Use hand-welding, flame-cutting, hand soldering, and brazing equipment to weld/join metal components, fill holes, indentations, or seams of fabricated metal products. There are around 1,100 of these workers are employed in the Oil Refining industry. You will find these workers welding components in flat, vertical or overhead positions. Common Job titles for this position are Maintenance Welder, Mig Welder, and Welder/Fabricator
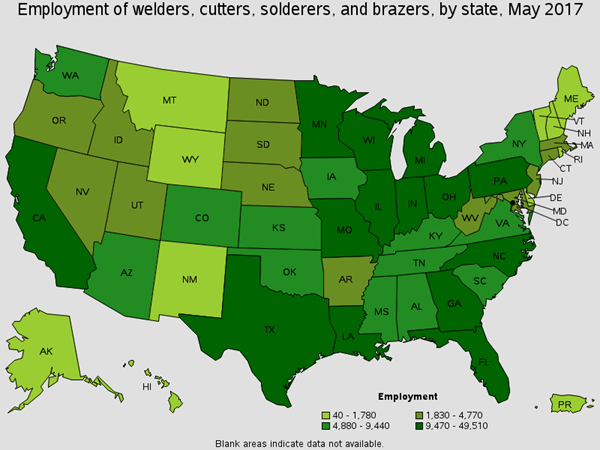
Employment of Welders, Cutters, Solderers, and Brazers
Operate welding, soldering or brazing machines that weld, braze, or heat treat metal products. Oil Refining Operations employ around 1,100 of these workers. You will find these workers adding material to work pieces, joining metal components, and annealing finished work pieces. Common Job titles for this position are Fabricator, Mig Welder, Spot Welder, Fitter-Welder, and Braze Operators.
A peak period for refineries occurs during planned maintenance schedules. Fall, winter, and spring seasons bring weather changes, along with heightened employment and work activities across many US refineries. Planned shutdowns are required for routine maintenance, such as furnace and tank cleaning, abrasive blasting, catalyst removal, insulation removal, draining pipes, and a lot of cutting/welding.
Plant turnarounds require careful planning, scheduling, and may present rippling effects across supply chains. Most importantly, extra safety precautions need adhered to because of deviated routine operations.
For all those working in or supporting refineries, we thought it would be helpful highlighting peak shutdown periods, specifically for Crude distillation. An entire turnaround schedule is shown below for refineries across US regions.
January to April are the most active months for turnarounds on the gulf coast, with February being the most active. Due to the refinery output of this region, there is a high number of outages.
| Thousand Barrels Per Day | As Percentage of Capacity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages | 2008-17 average planned outages | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages |
| December | 8 | 31 | 61 | 0% | 0% |
| January | 238 | 756 | 445 | 2% | 7% |
| February | 646 | 785 | 673 | 6% | 8% |
| March | 569 | 567 | 543 | 6% | 5% |
| April | 293 | 379 | 310 | 3% | 4% |
April is the most active time for shutdowns on the east coast.
| Thousand Barrels Per Day | As Percentage of Capacity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages | 2008-17 average planned outages | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages |
| December | 0 | 41 | 73 | 0% | 3% |
| January | 0 | 41 | 80 | 0% | 3% |
| February | 0 | 218 | 119 | 0% | 16% |
| March | 68 | 311 | 186 | 5% | 23% |
| April | 193 | 95 | 90 | 14% | 7% |
| May | 90 | 4 | 46 | 7% | 0% |
| June | 0 | 0 | 38 | 0% | 0% |
March and April are peak months for turnarounds.
| Thousand Barrels Per Day | As Percentage of Capacity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages | 2008-17 average planned outages | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages |
| December | 0 | 0 | 60 | 0% | 0% |
| January | 0 | 0 | 54 | 0% | 0% |
| February | 82 | 0 | 100 | 2% | 0% |
| March | 500 | 187 | 315 | 12% | 4% |
| April | 294 | 141 | 306 | 7% | 3% |
| May | 61 | 116 | 173 | 1% | 3% |
| June | 8 | 26 | 91 | 0% | 1% |
March and April are peak months for refineries located across the Rocky Mountain States.
| Thousand Barrels Per Day | As Percentage of Capacity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages | 2008-17 average planned outages | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages |
| December | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0% | 0% |
| January | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0% | 0% |
| February | 0 | 0 | 8 | 0% | 0% |
| March | 74 | 0 | 42 | 10% | 0% |
| April | 118 | 18 | 58 | 16% | 2% |
| May | 47 | 55 | 25 | 6% | 8% |
| June | 48 | 20 | 21 | 6% | 3% |
January and February are peak months for refinery turnarounds.
| Thousand Barrels Per Day | As Percentage of Capacity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages | 2008-17 average planned outages | Dec-17 to Jun-18 planned outages | Dec-16 to Jun-17 planned outages |
| December | 0 | 147 | 27 | 0% | 5% |
| January | 278 | 163 | 92 | 9% | 5% |
| February | 226 | 259 | 129 | 7% | 8% |
| March | 0 | 107 | 98 | 0% | 3% |
| April | 195 | 0 | 149 | 6% | 0% |
| May | 38 | 120 | 156 | 1% | 4% |
| June | 40 | 195 | 88 | 1% | 6% |
Refining oil and gas often involves multifaceted equipment, extreme temperatures and the need for handling hazardous materials. Inherent hazards ranging from chemicals, to explosions, and fires are constant concerns for those working at a refinery.
Thankfully, refineries are the least ranked Oil and Gas sub-industry for experiencing injuries. For every 100 employees, there are only .5 incidents, validation that safety managers are hard at work keeping workers safe.
"Nothing is of greater importance that the conservation of human life."
Nothing is greater than conserving life, especially for those who choose to make a living working across US refineries. As Rockefeller was quoted above, every man is owed that opportunity. When one is making a living, it should be done safely.
At MCR Safety, We Protect People! Let us keep you safe from the many hazards encountered at a refinery.
Find the right MCR Safety product that protects you against these common hazards.

Installing and repairing electrical wiring is common at an oil refinery. MCR Safety’s ARC Rated safety gear is built to last.
Learn More About ARC Gear ProtectionCommon Applications:

Workers transport many materials during refinery turnarounds. Heavy-duty wearing gloves are all these workers require!
Learn More About Abrasive Handling ProtectionCommon Applications:

Working around acids, additives, corrosives, solvents and wastewater puts you in direct contact with toxic substances, such as citric and HCI Acids, ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, benzene, and hydrogen fluoride. Be sure to check out our chemical permeation database.
Learn More About Chemicals and Liquids ProtectionCommon Applications:

56% of all recordable incidents in 2014 for Oil & Gas were attributed to "struck by" and "caught between” objects. Refinery work will quickly bang up a worker’s back-of-hands. Impact protection is a worker’s best friend. Are you ready for the new standard?
Learn More About Crush and Impact Protection
Installing and removing equipment during turnarounds requires welding gear.
Learn More About Cutting and Welding ProtectionCommon Applications:

Refineries create a lot of dust during turnaround season. Lined eyewear will keep it out of your eyes.
Learn More About Dust Protection
The principal hazard during refinery maintenance and shutdowns are flash fires. Max Comfort FR gear keeps Oil and Gas workers safe!
Learn More About Fire and Explosion ProtectionCommon Applications:
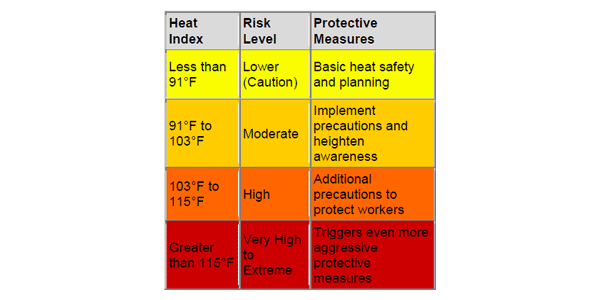
Breathable raingear, gloves and safety vests are necessary PPE when working in hot refining areas.
Learn More About Heat ProtectionCommon Applications:

Arsenic, hydrogen sulphide and polluted water are real concerns. Contractors deserve only the best PPE! Max 6 Goggles, Face Shields and clothing.
Common Applications:

Water spray, chemical slashes, and flying debris are only a few of the reasons why safety glasses must be worn.
Learn More About Impaired Vision ProtectionCommon Applications:

You will need heavy-duty gloves, well-fitted eyewear and goggles, and coveralls when installing and removing glasswool insulation.
Common Applications:

Many objects might fall on a worker’s hands and feet during maintenance on refineries. You are going to need steel toed boots working around the presence of water, chemical hazards, and dropped impact hazards.

Goggles, face shields and gloves are definitely needed during solvent based coating.

Cuts and lacerations make up 7 percent of all oil and gas injury claims. Metal shim is used in refineries for mounting motors and pumps. It is sharp, so you’ll need some safety gear that protects you from lacerations.
Learn More About Sharp Objects ProtectionCommon Applications:

10% of all eye injuries are the result of welding activities. Check out our filtered lens options.
Learn More About UV Radiation ProtectionCommon Applications:
 Why MCR Safety Products?
Why MCR Safety Products? 
MCR Safety manufactures and supplies Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Simply put, WE PROTECT PEOPLE! We are known world-wide for our extensive product line depth surrounding gloves, glasses, and garments spanning across numerous industries. We offer the total package of safety gear encompassing industrial gloves, safety glasses, protective garments, welding gear, industrial boots, Flame Resistant (FR) gear, face shields, and much more. From a glove standpoint alone, MCR Safety manufacturers and supplies over 1,000 different style gloves. Here are some of the many reasons MCR Safety is your go to source for PPE:
MCR Safety is recognized as a global manufacturer stretching across six countries, with both distribution and manufacturing facilities. Our core competency and specialty is manufacturing and supplying protective gloves, glasses, and garments. The information shown and provided on MCR Safety’s website, its safety articles, industry resource pages, highlighted hazards and safety equipment should be used only as a general reference tool and guide. The end user is solely responsible for determining the suitability of any product selection for a particular application. MCR Safety makes no guarantee or warranty (expressed or implied) of our products’ performance or protection for particular applications.